Product Description
Product features:
1.Carburizing by multi-purpose furnace, to lessen the deformatiion of gear surface, and lower noise.
2.Repeat technological process, to ensure the precision of gear surface, larger the contact area of planet gear& side gear surface, and average pressure better.
About us:
We are special and reliable manufacturer of V stay, torque rod, torque rod bush, repair kits, rubber support, differential assembly(differential case, gear, input/cross shaft etc.) and other truck parts
Products range:
European trucks: Mercedes benz, Volvo, Scania, MAN, DAF, RVI, Iveco.
Chinese trucks: Steyr, Howo, Faw, Xihu (West Lake) Dis.deng, ZheJiang , EQ153, Foton, CAMC, Kinglong, Golden Dragon, Yutong. Japanese trucks: Hino, Nissan,Mitsubish, Isuzu.
Korean trucks: Hyundai, KIA
We are a factory specialised in producing truck parts, chassis parts suitable for use in Japanese Truck, Sino Trucks and Euro Trucks.
We can custom make or with drawings/samples, OE numbers, We can produce the mould for making.
Work Flow & Products:
Contact infos:
Welcome you to conact us anytime! TAKE CHINAMFG TAKE SAFETY! /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1year |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Axle Number: | 2 |
| Application: | Truck |
| Certification: | CE, ISO |
| Material: | Steel |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
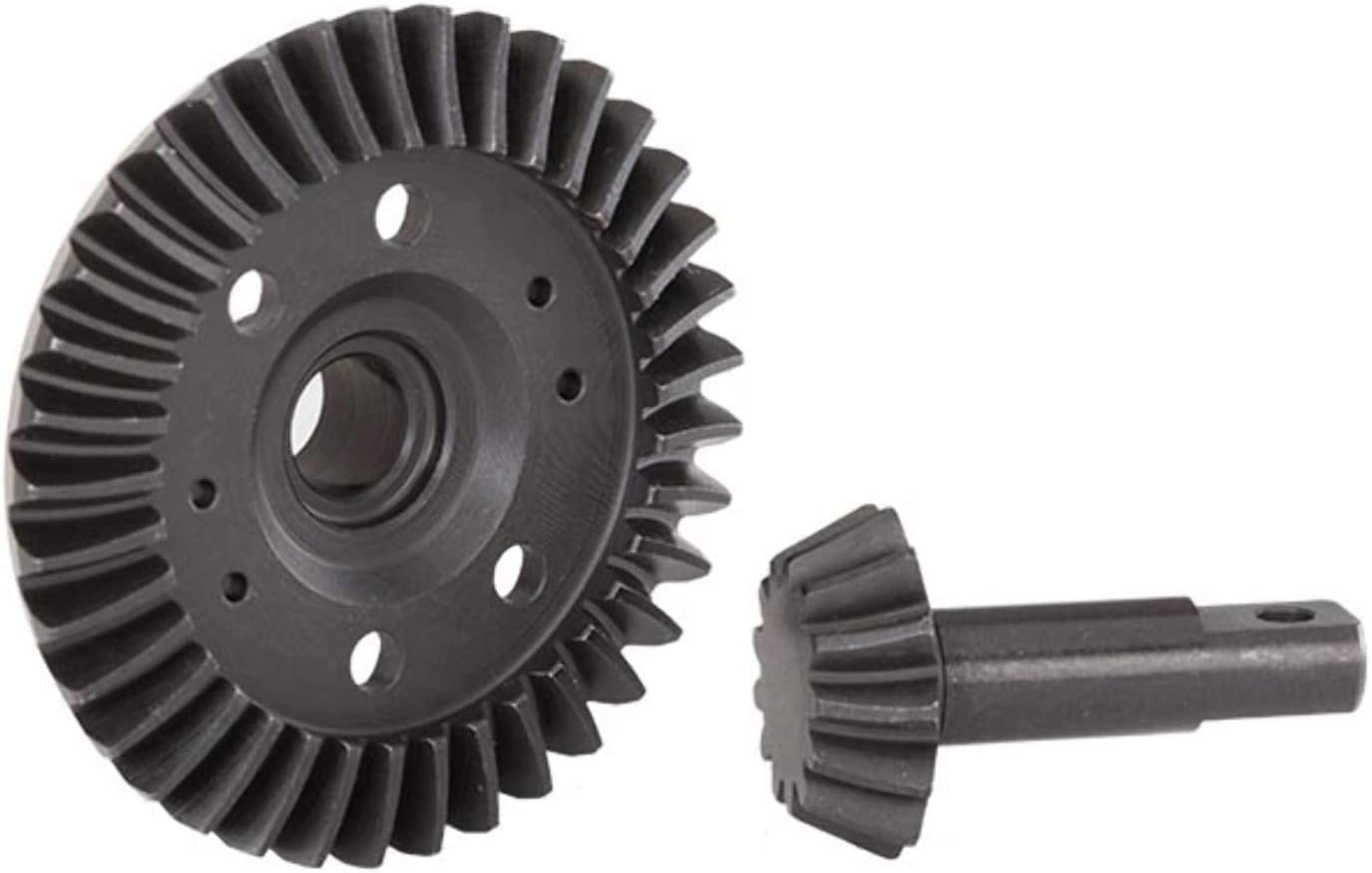

How does a differential gear system contribute to tire longevity?
A differential gear system plays a crucial role in tire longevity by ensuring optimal traction, minimizing tire wear, and distributing torque effectively. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a differential gear system contributes to tire longevity:
- 1. Traction Optimization: The differential gear system allows the wheels on the same axle to rotate at different speeds when the vehicle is turning. This capability helps improve traction and reduces tire scrubbing, which occurs when the tires resist turning and skid instead. By optimizing traction during turns, the differential gear system helps prevent excessive tire wear caused by scrubbing.
- 2. Torque Distribution: The differential gear system distributes torque from the engine to the wheels, allowing each wheel to receive an appropriate amount of power based on traction conditions. This distribution helps prevent wheel spin and excessive tire wear. By ensuring that torque is evenly distributed, the differential gear system helps maintain balanced tire wear across all wheels.
- 3. Wheel Speed Synchronization: When driving in a straight line, the differential gear system synchronizes the rotational speeds of the wheels. This synchronization minimizes tire scrubbing and reduces uneven wear. By keeping the wheels rotating at similar speeds, the differential gear system promotes even tire wear, extending tire longevity.
- 4. Cornering Stability: During cornering, the differential gear system allows the outer wheel to rotate faster than the inner wheel. This speed difference is necessary to accommodate the varying distances each wheel travels around the curve. By enabling smooth and controlled cornering, the differential gear system helps prevent excessive tire wear caused by lateral forces.
- 5. Reduced Stress on Tires: A properly functioning differential gear system helps reduce stress on tires by allowing them to rotate freely and independently. By mitigating excessive forces and minimizing tire scrubbing, the differential gear system helps decrease wear and tear on the tires. This reduction in stress contributes to prolonged tire life.
- 6. Traction Control: Some modern vehicles are equipped with advanced differential systems, such as electronic limited-slip differentials or torque vectoring differentials. These systems actively manage torque distribution to individual wheels based on traction conditions. By optimizing traction control, these differential systems help minimize tire slippage, improve grip, and reduce tire wear.
- 7. Proper Maintenance: Regular maintenance of the differential gear system is essential for tire longevity. This includes periodic inspection of the differential components, ensuring proper lubrication, and addressing any issues promptly. Well-maintained differentials help ensure optimal performance, reducing the risk of tire wear and extending tire life.
Overall, a well-functioning and properly maintained differential gear system plays a vital role in tire longevity. It optimizes traction, distributes torque effectively, synchronizes wheel speeds, promotes cornering stability, and reduces stress on tires. By understanding and maintaining the differential gear system, drivers can help maximize tire life and minimize the need for premature tire replacements.
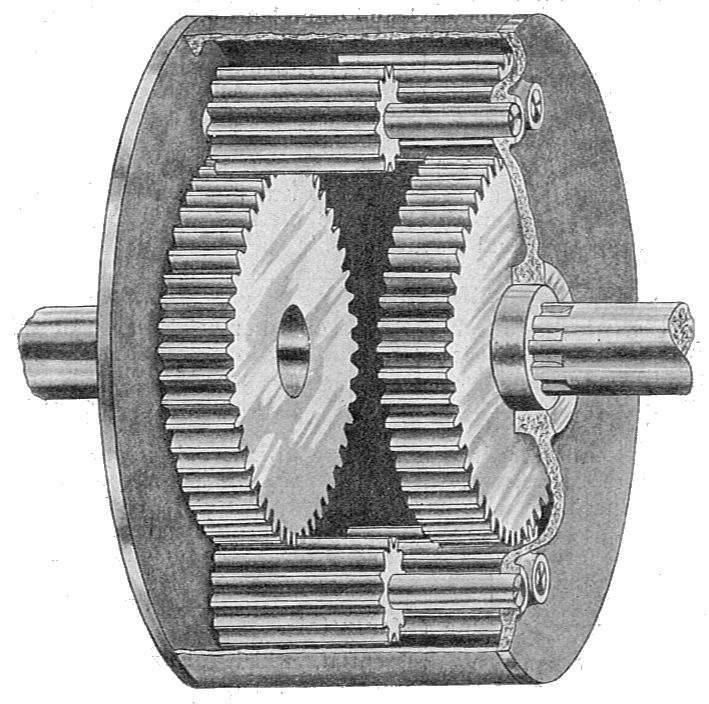
How do differential gears affect fuel efficiency in vehicles?
In vehicles, differential gears can have an impact on fuel efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how differential gears affect fuel efficiency:
- Gear Ratio: The gear ratio of the differential can affect fuel efficiency. A higher gear ratio (numerically lower) allows the engine to run at lower RPMs for a given speed, which can result in improved fuel efficiency. This is because the engine operates more efficiently in its lower RPM range, consuming less fuel. On the other hand, a lower gear ratio (numerically higher) can provide better acceleration and performance but may result in higher fuel consumption.
- Friction and Efficiency Losses: Differential gears introduce friction and mechanical losses in the drivetrain. As power is transmitted from the engine to the wheels through the differential, some energy is lost due to friction in the gears, bearings, and other components. These frictional losses reduce overall efficiency and can have a slight impact on fuel consumption. However, modern differentials are designed with efficiency in mind, and advancements in lubrication, materials, and manufacturing techniques help minimize these losses.
- Limited-Slip Differentials (LSD): Limited-slip differentials (LSDs) can have a minor effect on fuel efficiency compared to open differentials. LSDs use additional mechanisms to distribute torque between wheels, resulting in a slight increase in mechanical losses and energy consumption. However, the impact on fuel efficiency is generally minimal and may not be noticeable in everyday driving situations.
- Driving Style and Traction: The traction characteristics of differential gears can indirectly influence fuel efficiency. In slippery conditions or situations where wheelspin occurs, open differentials may allow excessive power to be lost in wheel slip, resulting in reduced traction and poorer fuel efficiency. Limited-slip differentials or advanced traction control systems can minimize wheel slip and improve overall traction, leading to better fuel efficiency by reducing power wastage.
- Vehicle Type and Design: The impact of differential gears on fuel efficiency can vary depending on the vehicle type and design. Factors such as weight, aerodynamics, tire type, transmission, and overall drivetrain configuration play a significant role in determining fuel efficiency. While differential gears are a part of the drivetrain, their influence on fuel efficiency needs to be considered in conjunction with other vehicle characteristics.
In summary, differential gears can affect fuel efficiency in vehicles primarily through their gear ratio, friction and efficiency losses, and traction characteristics. While the impact on fuel efficiency is generally modest, optimizing the gear ratio and minimizing frictional losses can contribute to improved fuel economy. Additionally, the traction benefits provided by limited-slip differentials or advanced traction control systems can indirectly enhance fuel efficiency by reducing power wastage in wheel slip situations.
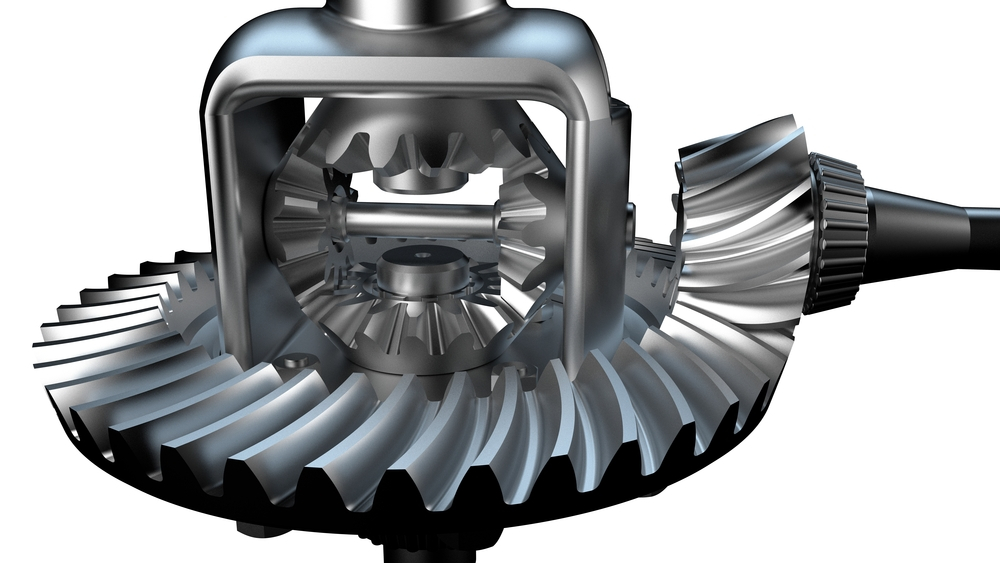
What is a differential gear and how does it work?
A differential gear is a component found in vehicles that allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds while receiving power from the engine. Here’s a detailed explanation:
A differential is commonly used in cars, trucks, and other vehicles with driven wheels. Its primary function is to distribute torque (rotational force) from the engine to the wheels while compensating for differences in wheel speeds, especially during turns or when driving on uneven surfaces.
Basic Structure:
A typical differential gear consists of several key components:
- Differential Case: It is the outer housing that encloses the differential assembly.
- Ring Gear: The ring-shaped gear located on the inside of the differential case.
- Pinion Gear: The small gear connected to the driveshaft, which meshes with the ring gear.
- Side Gears: Two gears connected to the axle shafts, which mesh with the pinion gear.
- Spider Gears (Planetary Gears): These gears are positioned between the side gears and allow the wheels to rotate at different speeds.
Function and Operation:
When power is transmitted from the engine to the differential, the pinion gear receives the rotational force from the driveshaft and meshes with the ring gear. As the pinion gear rotates, it rotates the ring gear and, in turn, the differential case.
During straight-line driving, when both wheels have equal traction and are rotating at the same speed, the spider gears rotate freely on their respective shafts. This allows the side gears to rotate at the same speed as the differential case, transmitting equal torque to both wheels.
However, when the vehicle turns or one wheel encounters a different traction condition (such as being on a slippery surface), the wheels need to rotate at different speeds. In this situation, the spider gears are forced to rotate along with the side gears due to the difference in rotational speeds between the two wheels.
As the spider gears rotate, they allow the side gears to rotate at different speeds, compensating for the variation in wheel speeds. This enables the wheels to rotate independently while still receiving power from the differential. The differential allows the outer wheel (on the outside of the turn) to rotate at a higher speed while the inner wheel (on the inside of the turn) rotates at a slower speed.
The differential gear system ensures smooth power delivery to the wheels, improves vehicle stability during turns, and reduces tire wear and stress on the drivetrain components.
It’s important to note that there are different types of differentials, such as open differentials, limited-slip differentials, and locking differentials. Each type has its own characteristics and is suited for different driving conditions and vehicle types.
In summary, a differential gear is a crucial component in vehicles that allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds while distributing power from the engine. By utilizing a combination of gears, it enables smooth and efficient power transmission to the wheels, particularly during turns or when encountering varying traction conditions.


editor by CX 2024-03-29