Product Description
high quality t slot gear rack plastic POM small differential gear
high quality t slot gear rack plastic POM small differential gear
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Soft Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | Internal Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Cast Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Nylon |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
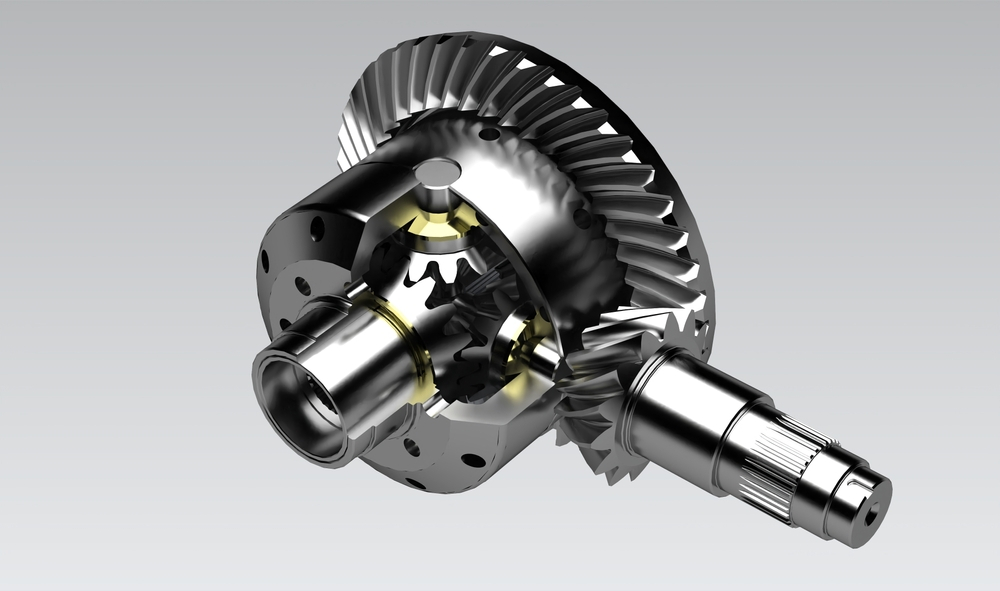
How do differential gears handle varying speeds in a vehicle’s wheels?
A differential gear system is designed to handle varying speeds in a vehicle’s wheels, allowing them to rotate at different rates while maintaining torque distribution. Here’s a detailed explanation of how differential gears achieve this:
1. Differential Assembly:
The differential assembly consists of several gears, including the ring and pinion gears, side gears, and spider gears. These components work together to accommodate varying speeds between the wheels.
2. Power Input:
The power is delivered to the differential gears through the driveshaft or transmission. The ring gear receives this power from the driveshaft, while the pinion gear is connected to the ring gear and transfers the rotational force to the differential assembly.
3. Speed Differences:
When a vehicle is moving in a straight line, the wheels ideally rotate at the same speed. However, during turns or when encountering different traction conditions, the wheels need to rotate at varying speeds. This is because the wheel on the outside of a turn covers a greater distance than the inside wheel, resulting in a speed differential.
4. Spider Gears:
The differential gears utilize spider gears, which are small gears located between the side gears. Spider gears allow the side gears to rotate independently of each other, accommodating the speed differences between the wheels.
5. Torque Distribution:
As the spider gears allow the side gears to rotate independently, torque is distributed between the wheels based on their speed differences. The wheel with less resistance or greater traction receives more torque, while the wheel with more resistance or lower traction receives less torque.
6. Smooth Cornering:
During turns, the inside wheel needs to rotate at a slower speed than the outside wheel. The differential gears allow this speed differentiation, enabling smooth cornering without wheel hop or tire scrubbing. By distributing torque appropriately, the differential gears ensure that both wheels receive sufficient power for optimal traction and control.
7. Limited-Slip and Locking Differentials:
In certain differential systems, such as limited-slip differentials or locking differentials, additional mechanisms are employed to further regulate speed differences and torque distribution. Limited-slip differentials use clutch packs or friction plates to provide a predetermined amount of resistance, allowing some differentiation between the wheels while still transferring power. Locking differentials lock the side gears together, ensuring equal torque distribution to both wheels, regardless of traction conditions.
8. Differential Types:
There are different types of differentials, including open differentials, limited-slip differentials, electronic differentials, torque vectoring differentials, and more. Each type utilizes specific technologies and mechanisms to handle varying speeds and torque distribution based on the vehicle’s requirements and driving conditions.
In summary, differential gears handle varying speeds in a vehicle’s wheels by utilizing a system of gears, including spider gears, side gears, ring and pinion gears. The speed differences between the wheels are accommodated by allowing independent rotation of the side gears through the spider gears. Torque distribution is adjusted to ensure optimal traction and control during turns and varying traction conditions. Additional mechanisms, such as limited-slip or locking differentials, can further regulate speed differences and torque distribution for enhanced performance and stability.
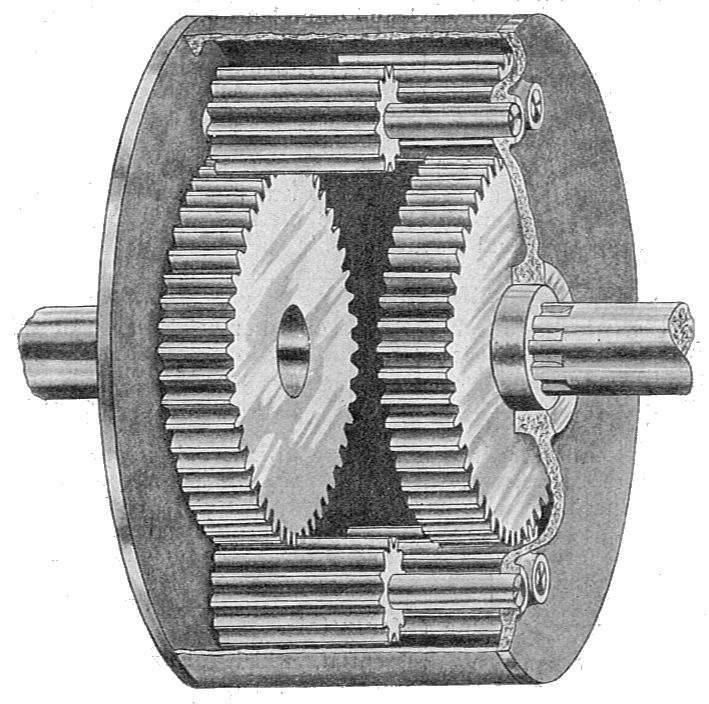
How do differential gears function in both front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles?
In both front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles, differential gears serve the same fundamental purpose of distributing power from the engine to the wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds. However, their specific configurations and functions differ between these two types of drivetrains. Here’s a detailed explanation of how differential gears function in both front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles:
Front-Wheel-Drive Vehicles:
In front-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are typically integrated into the transaxle assembly, which combines the transmission and differential into a single unit. Here’s how the differential gears function in front-wheel-drive vehicles:
- Power Input: The engine’s power is transmitted through the transmission to the transaxle assembly.
- Ring and Pinion Gears: The power from the transaxle is delivered to a set of ring and pinion gears within the differential assembly. These gears are responsible for distributing torque to the front wheels.
- Spider Gears: The ring gear is connected to a carrier that houses multiple smaller gears called spider gears. These spider gears allow the front wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns.
- Equal Torque Distribution: In front-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears prioritize equal torque distribution between the two front wheels. This design helps maintain traction and stability during acceleration and cornering.
- Traction Control: Some front-wheel-drive vehicles may also incorporate additional features in the differential assembly, such as electronic limited-slip differentials or traction control systems. These features help optimize traction by transferring power to the wheel with better grip, reducing wheel spin and improving overall performance.
Rear-Wheel-Drive Vehicles:
In rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are typically located in the rear axle assembly. Here’s how the differential gears function in rear-wheel-drive vehicles:
- Power Input: The engine’s power is transmitted through the transmission to the driveshaft, which connects to the rear axle assembly.
- Drive Pinion and Ring Gear: The driveshaft is connected to a drive pinion gear, which meshes with a larger ring gear. This gear set is responsible for transferring power to the rear wheels.
- Spider Gears: Similar to front-wheel-drive vehicles, rear-wheel-drive vehicles also have spider gears housed within the differential assembly. The spider gears allow the rear wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns.
- Torque Distribution: In rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears distribute torque to the rear wheels in a manner that prioritizes rear-wheel traction and propulsion. This configuration is particularly beneficial for vehicle acceleration and load-carrying capability.
- Enhanced Features: Rear-wheel-drive vehicles may also incorporate advanced differential systems, such as limited-slip differentials or electronic locking differentials, to optimize traction and performance. These features help improve grip, especially in challenging driving conditions or when driving off-road.
In summary, differential gears function differently in front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles due to their distinct drivetrain configurations. In front-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are typically integrated into the transaxle assembly and prioritize equal torque distribution to the front wheels. In rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are located in the rear axle assembly and focus on torque distribution to the rear wheels for propulsion. Understanding the specific functions of differential gears in each drivetrain type is essential for optimizing vehicle performance, traction, and stability.
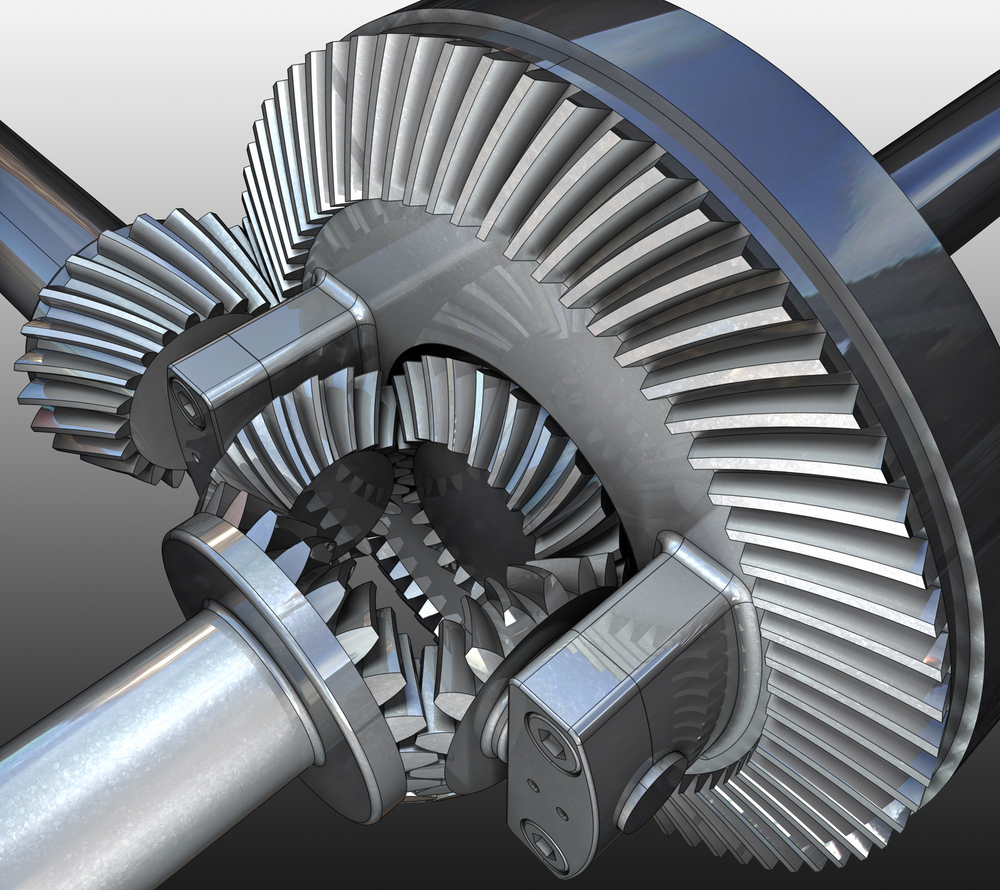
How does a differential gear help in turning a vehicle smoothly?
A differential gear plays a crucial role in enabling smooth turning of a vehicle. Here’s a detailed explanation:
When a vehicle turns, the wheels on the outside of the turn travel a greater distance compared to the wheels on the inside. This difference in distance would cause significant strain and binding in the drivetrain if all the wheels were rigidly connected. The differential gear solves this problem by allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns, resulting in smooth and controlled maneuvering.
1. Speed Differentiation:
The differential gear allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds while still receiving power from the engine. As the vehicle turns, the outer wheel covers a greater distance and needs to rotate faster than the inner wheel. The differential enables this speed differentiation by distributing torque unequally between the two wheels, allowing them to rotate at different rates.
2. Path Following:
By allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds, the differential gear helps the vehicle follow the desired path during a turn. The outside wheel, which needs to cover a longer distance, rotates faster to maintain the vehicle’s trajectory. At the same time, the inside wheel rotates slower, preventing the vehicle from skidding or drifting wide during the turn. The differential ensures that both wheels work together to maintain stability and control throughout the turning process.
3. Smooth Power Transfer:
During a turn, the differential gear facilitates smooth power transfer to the wheels. By allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds, the differential minimizes drivetrain stress and wheel scrubbing. This promotes smoother operation and reduces the likelihood of wheel hop or wheel slip, resulting in improved traction and overall control.
4. Reduction of Tire Wear:
The differential gear’s ability to differentiate wheel speeds during turns helps reduce tire wear. If the wheels were rigidly connected, they would experience excessive scrubbing and wear during turning maneuvers. The differential allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds, minimizing tire scrubbing and promoting more even tire wear. This contributes to longer tire life and better overall performance.
5. Enhanced Maneuverability:
By enabling smooth turning, the differential gear enhances the maneuverability of a vehicle. It allows for precise and controlled steering inputs, making it easier to navigate corners, curves, and tight spaces. The differential’s role in differentiating wheel speeds ensures that the vehicle can execute turns smoothly and responsively, enhancing the overall driving experience.
In summary, the differential gear helps in turning a vehicle smoothly by allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns. This speed differentiation enables the vehicle to follow the desired path, facilitates smooth power transfer, reduces tire wear, and enhances maneuverability. The differential’s ability to accommodate varying wheel speeds ensures that the vehicle can navigate turns with improved stability, control, and comfort.


editor by Dream 2024-05-06