Product Description
Excellent powder metallurgy parts metallic sintered parts
We could offer various powder metallurgy parts including iron based and copper based with top quality and cheapest price, please only send the drawing or sample to us, we will according to customer’s requirement to make it. if you are interested in our product, please do not hesitate to contact us, we would like to offer the top quality and best service for you. thank you!
How do We Work with Our Clients
1. For a design expert or a big company with your own engineering team: we prefer to receive a fully RFQ pack from you including drawing, 3D model, quantity, pictures;
2. For a start-up company owner or green hand for engineering: just send an idea that you want to try, you don’t even need to know what casting is;
3. Our sales will reply you within 24 hours to confirm further details and give the estimated quote time;
4. Our engineering team will evaluate your inquiry and provide our offer within next 1~3 working days.
5. We can arrange a technical communication meeting with you and our engineers together anytime if required.
| Place of origin: | Jangsu,China |
| Type: | Powder metallurgy sintering |
| Spare parts type: | Powder metallurgy parts |
| Machinery Test report: | Provided |
| Material: | Iron,stainless,steel,copper |
| Key selling points: | Quality assurance |
| Mould type: | Tungsten steel |
| Material standard: | MPIF 35,DIN 3571,JIS Z 2550 |
| Application: | Small home appliances,Lockset,Electric tool, automobile, |
| Brand Name: | OEM SERVICE |
| Plating: | Customized |
| After-sales Service: | Online support |
| Processing: | Powder Metallurgr,CNC Machining |
| Powder Metallurgr: | High frequency quenching, oil immersion |
| Quality Control: | 100% inspection |
The Advantage of Powder Metallurgy Process
1. Cost effective
The final products can be compacted with powder metallurgy method ,and no need or can shorten the processing of machine .It can save material greatly and reduce the production cost .
2. Complex shapes
Powder metallurgy allows to obtain complex shapes directly from the compacting tooling ,without any machining operation ,like teeth ,splines ,profiles ,frontal geometries etc.
3. High precision
Achievable tolerances in the perpendicular direction of compacting are typically IT 8-9 as sintered,improvable up to IT 5-7 after sizing .Additional machining operations can improve the precision .
4. Self-lubrication
The interconnected porosity of the material can be filled with oils ,obtaining then a self-lubricating bearing :the oil provides constant lubrication between bearing and shaft ,and the system does not need any additional external lubricant .
5. Green technology
The manufacturing process of sintered components is certified as ecological ,because the material waste is very low ,the product is recyclable ,and the energy efficiency is good because the material is not molten.
FAQ
Q1: What is the type of payment?
A: Usually you should prepay 50% of the total amount. The balance should be pay off before shipment.
Q2: How to guarantee the high quality?
A: 100% inspection. We have Carl Zeiss high-precision testing equipment and testing department to make sure every product of size,appearance and pressure test are good.
Q3: How long will you give me the reply?
A: we will contact you in 12 hours as soon as we can.
Q4. How about your delivery time?
A: Generally, it will take 25 to 35 days after receiving your advance payment. The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order. and if the item was non standard, we have to consider extra 10-15days for tooling/mould made.
Q5. Can you produce according to the samples or drawings?
A: Yes, we can produce by your samples or technical drawings. We can build the molds and fixtures.
Q6: How about tooling Charge?
A: Tooling charge only charge once when first order, all future orders would not charge again even tooling repair or under maintance.
Q7: What is your sample policy?
A: We can supply the sample if we have ready parts in stock, but the customers have to pay the sample cost and the courier cost.
Q8: How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
A: 1. We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit ;
2. We respect every customer as our friend and we sincerely do business and make friends with them, no matter where they come from.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car, as Required |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 20/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
How does a helical gear impact the overall efficiency of a system?
A helical gear has a significant impact on the overall efficiency of a system. Due to their unique design and characteristics, helical gears offer several advantages that contribute to improved efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a helical gear impacts the overall efficiency of a system:
- Power Transmission: Helical gears provide efficient power transmission due to their inclined tooth design. The helical teeth engage gradually, resulting in a smooth transfer of torque between the gears. This gradual engagement reduces impact and shock loads, minimizing energy losses and improving overall efficiency.
- Load Distribution: The helical tooth profile allows for increased contact area between the gear teeth compared to other gear types. This larger contact area results in improved load distribution across the gear teeth. By distributing the load more evenly, helical gears can handle higher loads without excessive wear and reduce the risk of tooth failure, leading to increased efficiency and reliability.
- Noise and Vibration Reduction: Helical gears operate with less noise and vibration compared to other gear types, such as spur gears. The inclined tooth profile of helical gears helps to minimize gear meshing noise and vibration by distributing the forces along the gear teeth over a larger contact area. Reduced noise and vibration levels contribute to a quieter and smoother operation, indicating lower energy losses and improved overall efficiency.
- Higher Gear Ratios: Helical gears can achieve higher gear ratios compared to other gear types. This capability allows for more precise speed control and torque conversion in various applications. By providing the desired gear ratios, helical gears enable the system to operate at optimal speeds and torque levels, maximizing efficiency and performance.
- Efficient Lubrication: The helical gear design allows for effective lubrication of the gear teeth. The continuous sliding action between the helical teeth assists in distributing the lubricant evenly along the gear contact surfaces. Proper lubrication reduces friction and wear, minimizing energy losses and enhancing the overall efficiency of the gear system.
- Compact Design: Helical gears have a compact design that allows for efficient use of space within a system. The inclined tooth profile enables multiple gear sets to be positioned on parallel or intersecting shafts, facilitating compact gear arrangements. This compactness reduces the overall size and weight of the system while maintaining high efficiency.
- High Precision: Helical gears offer excellent positional accuracy and repeatability. The helical tooth profile ensures precise and consistent gear meshing, resulting in accurate motion control and minimal backlash. This precision contributes to efficient operation, especially in applications requiring precise positioning and synchronization of components.
- Wear Resistance: Helical gears exhibit good wear resistance due to the larger contact area and gradual tooth engagement. The inclined tooth profile helps distribute the load, reducing localized wear and extending the gear’s service life. Reduced wear translates to sustained gear efficiency over time, minimizing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
Overall, the design characteristics of helical gears, including smooth power transmission, load distribution, noise reduction, higher gear ratios, efficient lubrication, compactness, precision, and wear resistance, collectively contribute to improved system efficiency. By choosing helical gears appropriately for a given application, engineers can enhance the overall performance, reliability, and energy efficiency of the system.
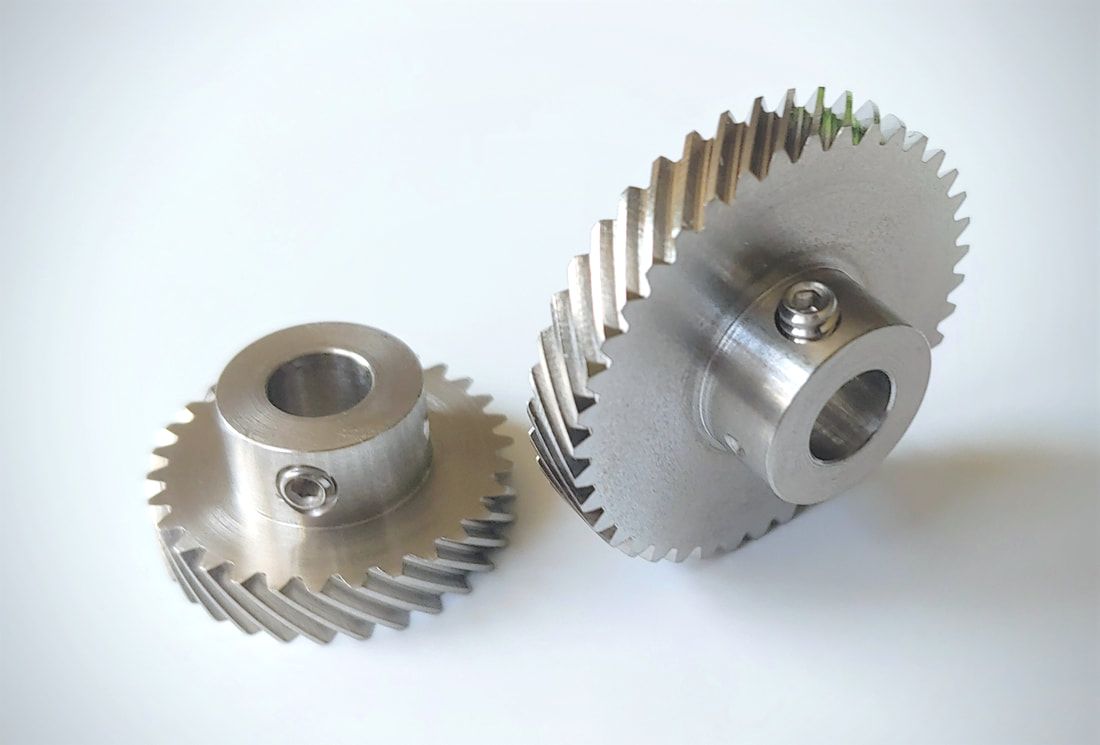

What are the potential challenges in designing and manufacturing helical gears?
Designing and manufacturing helical gears can present various challenges that need to be addressed to ensure optimal performance and durability. Here’s a detailed explanation of the potential challenges encountered in designing and manufacturing helical gears:
- Complex Geometry: The geometry of helical gears is more complex compared to other gear types. The helical tooth profile requires precise calculations and manufacturing techniques to achieve the desired gear performance. Designers must account for factors such as helix angle, lead angle, tooth shape modification, and tooth contact pattern optimization. The complex geometry adds challenges to both the design and manufacturing processes.
- Manufacturing Accuracy: Achieving the required manufacturing accuracy for helical gears can be challenging. The gear teeth must have precise profiles and dimensions to ensure proper meshing and load distribution. The manufacturing processes, such as gear cutting (e.g., hobbing or grinding), must be carefully controlled to achieve the desired tooth geometry, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy. Maintaining tight tolerances and minimizing manufacturing variations are crucial to ensure the gears meet the design specifications.
- Axial Thrust and Bearing Considerations: Helical gears generate axial thrust forces due to the helix angle. The axial thrust can affect gear performance and may require additional measures to properly manage. Adequate bearing selection and support systems must be designed to accommodate the axial loads and ensure smooth gear operation. Consideration should also be given to the potential thrust-induced axial movement and its impact on gear alignment and system performance.
- Noise and Vibration: Helical gears can produce noise and vibration during operation, particularly if not designed or manufactured correctly. Factors such as improper tooth contact, misalignment, or excessive gear backlash can contribute to increased noise and vibration levels. Designers and manufacturers must carefully analyze and optimize the gear geometry, tooth contact patterns, and manufacturing processes to minimize noise and vibration and ensure quieter operation.
- Lubrication Challenges: Proper lubrication is critical for the smooth operation and longevity of helical gears. However, the helical tooth profile can pose challenges for lubricant distribution. The inclined teeth create a sliding action that may affect lubricant film formation and retention. Ensuring adequate lubrication to all gear surfaces, including the tooth flanks and root fillets, becomes important. Designing efficient lubrication systems and selecting appropriate lubricants that can withstand the sliding action and provide sufficient film thickness is crucial.
- Heat Dissipation: Helical gears can generate significant heat during operation, especially at high speeds or under heavy loads. Effective heat dissipation is essential to prevent overheating and premature wear. Designers and manufacturers need to consider heat dissipation mechanisms, such as proper housing design, cooling methods, and suitable materials with good thermal conductivity. Adequate ventilation and lubrication systems should also be designed to facilitate heat dissipation and maintain optimum operating temperatures.
- Tooling and Equipment: Manufacturing helical gears often requires specialized tooling and equipment. The gear cutting processes, such as hobbing or grinding, may necessitate specific tools, cutters, or grinding wheels. These tools must be properly selected, calibrated, and maintained to achieve accurate tooth profiles and finishes. The availability of suitable tooling and equipment, as well as the expertise to operate and maintain them, can be a challenge for gear manufacturers.
- Cost Considerations: Designing and manufacturing helical gears can involve higher costs compared to simpler gear types. The complexity of gear geometry, precision manufacturing requirements, specialized tooling, and additional considerations such as bearing support or noise reduction measures can contribute to increased production costs. Balancing the desired gear performance with cost considerations can be challenging for designers and manufacturers.
By addressing these potential challenges through careful design, precise manufacturing processes, and proper selection of materials and lubrication, engineers can overcome the complexities associated with designing and manufacturing helical gears and ensure high-quality gears that meet performance requirements and deliver long-term reliability.

How do helical gears differ from other types of gears?
Helical gears possess distinct characteristics that set them apart from other types of gears. Here’s a detailed explanation of how helical gears differ from other gear types:
1. Tooth Orientation: Unlike spur gears, which have teeth perpendicular to the gear axis, helical gears have teeth that are cut at an angle to the gear axis. This helical tooth orientation enables gradual engagement and disengagement of the gear teeth, resulting in smoother and quieter operation.
2. Contact Pattern: Helical gears have a larger contact area compared to spur gears. The helical tooth design allows for multiple teeth to be in contact simultaneously, distributing the load across a broader surface. This increased contact pattern enhances load-carrying capacity and improves the gear’s ability to transmit higher torque.
3. Tooth Engagement: In helical gears, the teeth gradually mesh as they come into contact during rotation. This gradual engagement reduces the impact and noise typically associated with spur gears. The sliding action between the helical teeth also generates axial forces, resulting in a thrust load along the gear axis.
4. Load Distribution: The helical tooth orientation enables load distribution along the tooth face. This characteristic helps minimize localized stress concentrations and tooth wear, resulting in improved gear durability and longevity.
5. Power Transmission Efficiency: Helical gears offer high power transmission efficiency due to their larger contact area and gradual tooth engagement. The sliding action between the teeth introduces some axial force and axial thrust, which must be properly supported, but overall, helical gears are efficient in transmitting power.
6. Parallel Shaft Alignment: Helical gears are primarily used for parallel shaft applications. They transmit motion and power between parallel shafts with a constant speed ratio. Other gear types, such as bevel gears or worm gears, are better suited for non-parallel shaft arrangements or specific motion requirements.
7. Noise and Vibration: Compared to spur gears, helical gears produce less noise and vibration due to their gradual tooth engagement. The helical tooth design reduces the impact and noise caused by abrupt contact between gear teeth, resulting in smoother and quieter operation.
8. Manufacturing Complexity: Helical gears are more complex to manufacture compared to spur gears due to the helical tooth profile. The angled teeth require specialized cutting tools and machining processes. This complexity can affect the manufacturing cost and lead time of helical gears.
9. Axial Thrust Load: Helical gears generate axial forces and thrust loads due to the sliding action between the teeth. This axial thrust must be considered and properly supported in the gear system design to ensure smooth operation and prevent excessive wear or failure.
10. Application Range: Helical gears are versatile and find applications across various industries. They are commonly used in power transmission, robotics, machine tools, automotive systems, and other mechanical systems that require precise motion control and high torque transmission.
In summary, helical gears differ from other gear types in terms of tooth orientation, contact pattern, tooth engagement, load distribution, power transmission efficiency, shaft alignment suitability, noise and vibration characteristics, manufacturing complexity, axial thrust load, and application range. These unique characteristics make helical gears well-suited for specific applications where smooth operation, high load-carrying capacity, and precise motion control are required.


editor by Dream 2024-05-03