Product Description
Key attributes
Other attributes
Applicable Industries
Manufacturing Plant, Construction works , Energy & Mining
Weight (KG)
3000
Showroom Location
None
Video outgoing-inspection
Provided
Machinery Test Report
Provided
Marketing Type
Ordinary Product
Warranty of core components
Not Available
Core Components
Gear, Ring Gear
Place of CHINAMFG
ZheJiang , China
Condition
New
Warranty
1year
Shape
Ring Gear
Standard or Nonstandard
Nonstandard
Tooth Profile
Helical Gear,spur gear
Material
Steel
Processing
Forging
Pressure Angle
custom
Brand Name
TS
Product Name
Large Ring Gear
Module No.
5-180
Process
Milling,hobbing
Surface treatment
as request
Heat treatment
Q&T
Application
Industry machinery,transmission equipment
Standard
DIN ANSI ISO
Certificate
ISO
OEM Service
YES
Delivery time
15-60days
Packaging and delivery
Packaging Details
Package adapting to CHINAMFG transport
Port
ZheJiang ,HangZhou
Supply Ability
Supply Ability
5 Piece/Pieces per Month
OUR WORKSHOPS
OUR EQUIPMENTS
Technology Process
|
Material |
Carbon steel,Alloy steel |
||
|
Structure |
Forging,casting |
||
|
Type of gear |
spur gear,helical gear,Planetary Gear |
||
|
Heat treatment |
Quenching and tempering |
||
|
Process |
forging, rough machining, QT, finish machining |
||
|
Main equipments |
hobbing,CNC machine |
||
|
Module |
up to 200 |
||
|
Precision of gear |
Grinding ISO Grade 5-7 & Hobbing ISO Grade 8-9 |
||
|
Inspection |
Raw material inspection, UT,physical property test,dimension inspect |
||
|
Application |
Mining machinery, mill, kiln and other equipment |
||
OUR CERTIFICATE
OUR CUSTOMER FEEDBACK
CONTACT
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industry |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hb190-Hb300 |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
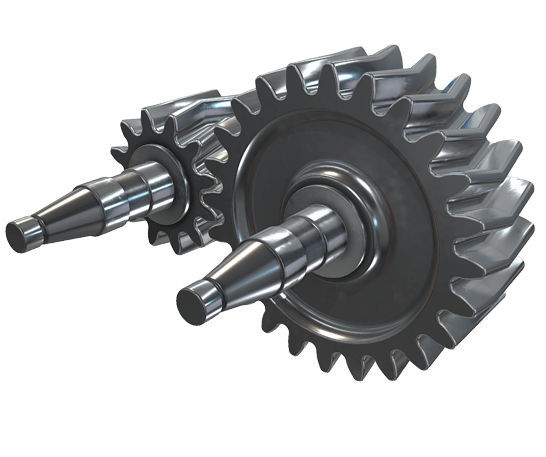
How do you choose the right size herringbone gear for your application?
Choosing the right size herringbone gear for your application involves considering several factors and performing engineering calculations. Here’s a detailed explanation of the steps involved in selecting the appropriate size herringbone gear:
- Determine the Application Requirements: Start by understanding the specific requirements of your application. Consider factors such as the input and output speeds, torque loads, power requirements, duty cycle, and operating conditions. Determine the desired service life, efficiency, and reliability expectations for the gear system.
- Calculate the Gear Ratios: Determine the required gear ratios based on the speed and torque requirements of your application. Gear ratios define the relationship between the rotational speeds and torques of the input and output shafts. Select appropriate gear ratios that fulfill the desired performance objectives.
- Calculate the Load and Torque: Estimate the maximum load and torque that the herringbone gear will experience during operation. Consider both static and dynamic loads, shock loads, and any potential overload conditions. Calculate the required torque capacity of the gear system based on these load considerations.
- Consider the Size and Space Constraints: Evaluate the available space and size constraints in your application. Measure the available distance for gear installation, including the gear’s diameter, width, and axial length. Consider any restrictions on the gear’s physical dimensions and ensure that the selected gear size fits within the available space.
- Determine the Gear Module: The gear module is a parameter that defines the size and number of gear teeth. Calculate the gear module based on the desired gear ratios, torque capacity, and available space. The gear module is typically determined by considering a balance between gear tooth strength, contact ratio, and manufacturing feasibility.
- Perform Gear Design Calculations: Utilize standard gear design formulas and calculations to determine the required number of gear teeth, pitch diameter, helix angles, and other gear dimensions. Consider factors such as gear tooth strength, contact ratio, tooth profile optimization, and gear manufacturing standards. These calculations ensure that the selected gear size can handle the anticipated loads and provide reliable performance.
- Consult Manufacturers and Standards: Consult gear manufacturers, industry standards, and guidelines to ensure compliance with best practices and safety requirements. Manufacturers can provide technical expertise, recommend suitable gear sizes, and offer guidance on material selection, heat treatment processes, and gear quality standards.
- Consider Cost and Availability: Evaluate the cost implications and availability of the selected gear size. Consider factors such as material costs, manufacturing complexity, lead times, and the overall economic feasibility of the gear system. Balance the desired performance with cost considerations to arrive at an optimal gear size.
It’s important to note that selecting the right size herringbone gear requires expertise in gear design and engineering. If you lack the necessary knowledge, it is advisable to consult with experienced gear engineers or manufacturers who can assist in the selection process.
In summary, choosing the right size herringbone gear involves determining the application requirements, calculating gear ratios and torque loads, considering size constraints, determining the gear module, performing gear design calculations, consulting manufacturers and standards, and considering cost and availability. Following these steps ensures that the selected herringbone gear size meets the specific needs of your application and provides reliable and efficient operation.

What lubrication is required for herringbone gears?
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth and efficient operation of herringbone gears. The lubricant used in herringbone gear systems plays a crucial role in reducing friction, minimizing wear, dissipating heat, and protecting the gear surfaces. Here’s a detailed explanation of the lubrication requirements for herringbone gears:
- Lubricant Selection: When selecting a lubricant for herringbone gears, it is important to consider factors such as load, speed, operating temperature, and environmental conditions. The lubricant should have suitable viscosity and additives to provide adequate film thickness and maintain lubrication under the anticipated operating conditions. Commonly used lubricants for herringbone gears include mineral oils, synthetic oils, and specialty lubricants formulated for gear applications.
- Viscosity: The viscosity of the lubricant is crucial for ensuring proper lubrication and film formation between the gear teeth. The lubricant should have sufficient viscosity to create an effective lubricating film that separates the gear surfaces and reduces friction. It should be able to maintain this film under the operating conditions, ensuring smooth gear engagement and minimizing wear. The appropriate viscosity grade is typically specified by the gear system manufacturer based on the gear design, load, and speed.
- Lubricant Application: The lubricant should be applied to the gear system in the appropriate manner to ensure uniform coverage and distribution. In most cases, herringbone gears are lubricated by immersion or splash lubrication, where the gears partially or fully submerge in the lubricant or have the lubricant splashed onto their surfaces. The lubricant should be directed towards the gear meshing area to ensure proper lubrication of the gear teeth and contact surfaces.
- Lubricant Maintenance: Regular lubricant maintenance is essential to ensure the continued performance and longevity of herringbone gears. This includes monitoring the lubricant condition, checking for contamination, and replenishing or replacing the lubricant as necessary. Over time, the lubricant may degrade, become contaminated with particles or moisture, or lose its effectiveness. Regular inspections and lubricant analysis can help identify any issues and determine the appropriate maintenance intervals for lubricant replacement or replenishment.
- Sealing and Contamination Prevention: Proper sealing of the gear housing or enclosure is important to prevent the ingress of contaminants, such as dust, dirt, or moisture, into the gear system. Contaminants can degrade the lubricant and lead to increased wear and damage to the gear surfaces. Seals, gaskets, or other appropriate sealing mechanisms should be employed to minimize the risk of contamination and maintain the integrity of the lubricant.
It is important to consult the gear system manufacturer’s recommendations and specifications regarding lubrication requirements. The manufacturer may provide specific guidelines regarding lubricant type, viscosity, application methods, and maintenance procedures based on the gear design and intended operating conditions. Adhering to these guidelines will help ensure optimal lubrication and maximize the performance and service life of herringbone gears.

What is a herringbone gear and how does it work?
A herringbone gear, also known as a double helical gear, is a specialized type of gear with a unique tooth design. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a herringbone gear is and how it works:
A herringbone gear consists of two helical gear sections that are mirror images of each other and are joined together to form a V-shaped or herringbone-shaped tooth profile. Unlike conventional helical gears, which have a single helix angle and a continuous spiral tooth profile, herringbone gears have two opposing helix angles, resulting in a “V” shape when viewed from the end.
The primary advantage of the herringbone gear design is its ability to eliminate axial thrust or end thrust forces that are generated in helical gears. In a conventional helical gear, the helix angle of the teeth causes an axial force along the gear’s axis during rotation. This axial force can create significant thrust loads that need to be counteracted using thrust bearings or other mechanisms.
By using the double helix design of herringbone gears, the opposing helix angles cancel out the axial forces generated by each helical section. This cancellation of axial forces eliminates the need for thrust bearings and allows herringbone gears to transmit torque smoothly without axial movement or thrust loads.
When a herringbone gear is in operation, the angled teeth of the two helical sections engage with each other, similar to how helical gears mesh. The contact between the teeth occurs gradually, starting from one end of the gear and progressing towards the other end. The overlapping or interlocking tooth profiles ensure a continuous and smooth transfer of power.
The herringbone gear design offers several advantages:
- Axial Load Balancing: The opposing helix angles in herringbone gears balance out the axial forces, eliminating the need for thrust bearings and reducing wear on the gear teeth.
- Increased Load Capacity: The V-shaped tooth profile of herringbone gears provides increased tooth contact area compared to a single helix gear. This leads to improved load distribution and higher load-carrying capacity.
- Reduced Vibration and Noise: The double helix design of herringbone gears helps cancel out vibrations and reduce noise during operation. The opposing helix angles minimize tooth deflection and ensure smoother engagement between the gear teeth.
- Bidirectional Power Transmission: Herringbone gears can transmit power in both directions due to their symmetrical tooth profiles. This makes them suitable for applications where reversing or bidirectional power transmission is required.
- High Efficiency: The continuous and gradual engagement of the herringbone gear teeth results in improved efficiency by reducing sliding friction and minimizing backlash.
Herringbone gears are commonly used in various industrial applications, including power transmission systems, heavy machinery, oil and gas equipment, marine propulsion systems, and high-speed gearboxes. Their unique design and benefits make them well-suited for applications that require high torque transmission, smooth operation, and minimal axial thrust.


editor by CX 2024-03-27