Product Description
Transmission Differential Gear for Gear Box
- Brief introduction:
- Hardness: Hard tooth surface, Soft tooth surface
Feature:High efficiency, Low noise and Wear resistance
1. Description
| No. | Item | Description |
| 1 | Name | Gear |
| 2 | Size | Products can be customized. |
| 3 | Testing Equipment | Rockwell hardness tester 500RA, Double mesh instrument HD-200B & 3102,Gear measurement center instrument CNC3906T and other High precision detection equipments |
| 4 | Certification | GB/T19001-2016/ISO9001:2015 |
| 5 | Usage | Used in printing machine, cleaning machine, medical equipment, garden machine, construction machine, electric car, valve, forklift, transportation equipment and various gear reducers.etc |
| 6 | Package | According to customer’s request |
2. Photos
HangZhou Zhihai Machinery Co., Ltd. is a professional engaged in the development, production, sales of all kinds of precision gear and mechanical transmission parts of the enterprise. The products are not only sold on the domestic market, but also exported to Europe and Southeast Asia.
Company’s main products are: All kinds of gear box for host plant supporting gear andtransmission parts. Especially suitable for mass production of modulus of 0.8 to 6straight gear, bevel gear, the inner gear ring and cone type (umbrella) gear, gearaccuracy from the standard 5-8 level.
3. Order process
a. Customer sends us the drawing or sample, If only sample, our company supply the CAD drawing.
b. Our company supplies the processing technique and quotation.
c. Our company supplies the sample after customer confirmed processing technique and quotation.
d. Customer places the order after confirm the sample.
e. Customer pay 50% deposit
f. Quantity production.
g. Pay the balance after the acceptance and confirmation.
h. Delivery.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Agricultural Machinery, Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Agricultural Machinery, Car, Truck |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface, Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear, External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Sintered Gear, Gear Hobbing, Gear Shaping and Gear Grinding |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear, Involute |
| Material: | Stainless Steel, 45#Steel, 20crmnti, 40cr, 20CrNiMo, 20mncr5, Gcr15simn |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
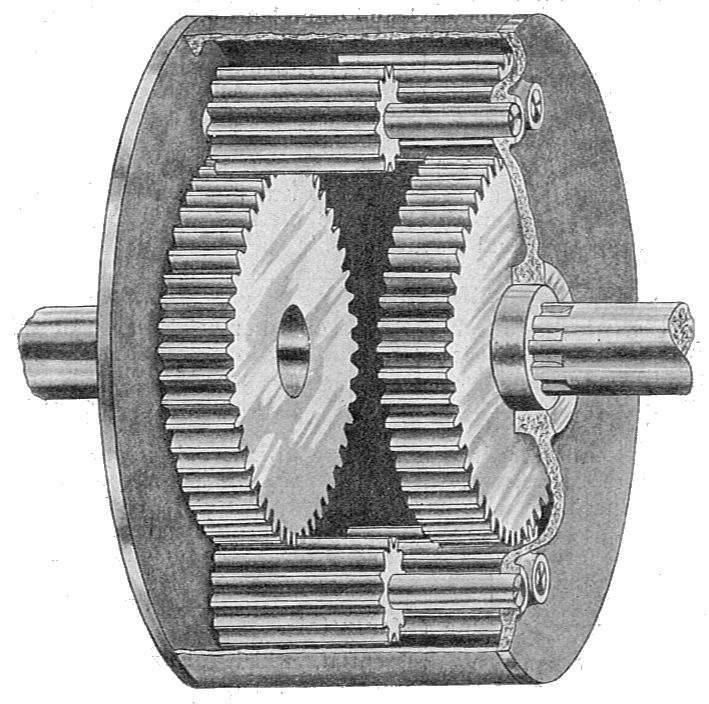
How do you maintain and service a differential gear?
Maintaining and servicing a differential gear is crucial to ensure its optimal performance and longevity. Here’s a detailed explanation of the maintenance and servicing process:
1. Regular Inspection:
Perform regular visual inspections of the differential gear to check for any signs of damage, leaks, or excessive wear. Look for oil leaks around the differential housing and inspect the driveshaft, axles, and seals for any signs of damage or leakage. Additionally, listen for any abnormal noises coming from the differential during operation, as they may indicate underlying issues.
2. Fluid Change:
Regularly change the differential fluid as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer. Over time, the fluid can become contaminated with debris, moisture, and metal particles, which can cause accelerated wear and reduced performance. Changing the fluid helps maintain proper lubrication and cooling of the differential gears. Refer to the vehicle’s owner manual or service guide for the recommended fluid type and change intervals.
3. Fluid Level Check:
Check the fluid level in the differential regularly to ensure it is within the recommended range. Use the appropriate method specified by the vehicle manufacturer to check the fluid level, such as a dipstick or inspection plug. Maintaining the correct fluid level is essential for proper lubrication and cooling of the gears.
4. Seal Replacement:
If you notice any leaks or damaged seals, it is important to replace them promptly. Leaking seals can lead to fluid loss, which can cause inadequate lubrication and potential damage to the differential gears. Replace seals as per the manufacturer’s recommendations and ensure proper installation to prevent future leaks.
5. Gear Inspection and Adjustment:
Periodically inspect the gears for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. If any issues are detected, consult a qualified technician or mechanic for further evaluation and adjustment. Gears that are excessively worn or damaged may need to be replaced to maintain the proper functioning of the differential.
6. Service Differential Components:
Some differential systems have additional components that require servicing. For example, limited-slip differentials may have clutch packs or friction plates that need periodic inspection and maintenance. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for servicing these components, which may involve cleaning, lubrication, or replacement as necessary.
7. Professional Servicing:
In addition to regular maintenance tasks, it is recommended to have the differential gear serviced by a professional technician or mechanic at specific intervals or when experiencing significant issues. Professional servicing may involve more in-depth inspections, adjustments, or repairs that require specialized tools and knowledge.
8. Follow Manufacturer Recommendations:
Always refer to the vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines for maintaining and servicing the differential gear. They provide specific instructions tailored to your vehicle’s make, model, and differential type, ensuring that you follow the appropriate procedures for optimal performance and longevity.
In summary, maintaining and servicing a differential gear involves regular inspections, fluid changes, fluid level checks, seal replacements, gear inspections and adjustments, servicing of differential components, professional servicing when necessary, and adherence to manufacturer recommendations. By following these steps, you can help ensure the proper functioning and durability of the differential gear in your vehicle.
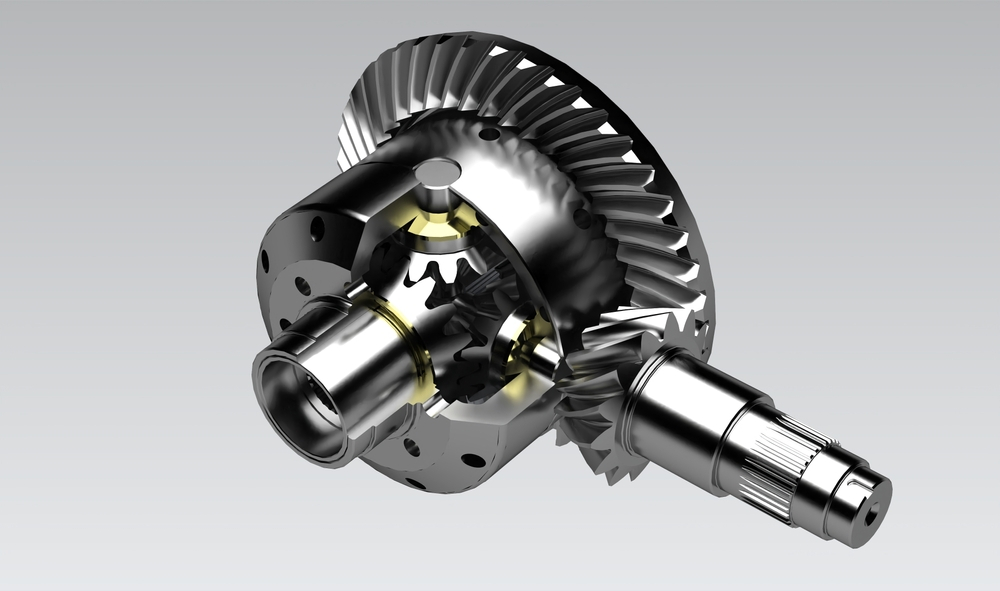
What are the considerations for choosing the right type of differential gear for a vehicle?
When selecting the appropriate type of differential gear for a vehicle, several considerations come into play. Choosing the right differential gear involves assessing factors such as vehicle characteristics, intended use, driving conditions, and desired performance. Here’s a detailed explanation of the considerations for choosing the right type of differential gear:
- Vehicle Type: The type of vehicle, whether it’s a passenger car, SUV, truck, or performance vehicle, plays a significant role in determining the appropriate differential gear. Different types of vehicles have varying weight distributions, power outputs, and handling characteristics, which influence the optimal choice of differential gear.
- Driving Conditions: The intended driving conditions are crucial in selecting the right differential gear. Factors such as road surface, weather conditions, and terrain should be considered. For example, vehicles driven primarily on paved roads may benefit from different differential gear options compared to off-road vehicles that frequently encounter challenging terrain or vehicles that operate in regions with snowy or icy conditions.
- Performance Requirements: The desired performance attributes of the vehicle are important considerations. Some drivers prioritize acceleration and high-speed performance, while others focus on off-road capabilities, towing capacity, or fuel efficiency. Differential gears can be chosen to optimize specific performance aspects, such as maximizing traction, improving handling, enhancing torque delivery, or achieving better fuel economy.
- Traction Needs: The level of traction required is a key factor in selecting the right differential gear. Vehicles that need maximum traction in challenging conditions, such as racing cars, off-road vehicles, or vehicles used in low-grip environments, may benefit from limited-slip differentials or locking differentials. These differential types help distribute power to the wheels with the most grip, enhancing traction and maintaining vehicle control.
- Driving Dynamics: The desired driving dynamics and handling characteristics also influence the choice of differential gear. Some drivers prefer a more predictable and balanced handling, while others may desire more aggressive cornering capabilities. Differential gears with specific characteristics, such as torque vectoring differentials, can enhance these driving dynamics by actively managing torque distribution between individual wheels.
- Budget: Cost considerations are also significant when choosing a differential gear. Different types of differential gears vary in terms of complexity, features, and pricing. It’s essential to evaluate the budget constraints and weigh the cost against the desired performance benefits and requirements.
In summary, selecting the right type of differential gear for a vehicle involves considering factors such as vehicle type, driving conditions, performance requirements, traction needs, driving dynamics, and budget. By carefully assessing these considerations, drivers can choose a differential gear that aligns with their vehicle’s characteristics, intended use, and performance objectives, ultimately enhancing traction, handling, and overall driving experience.
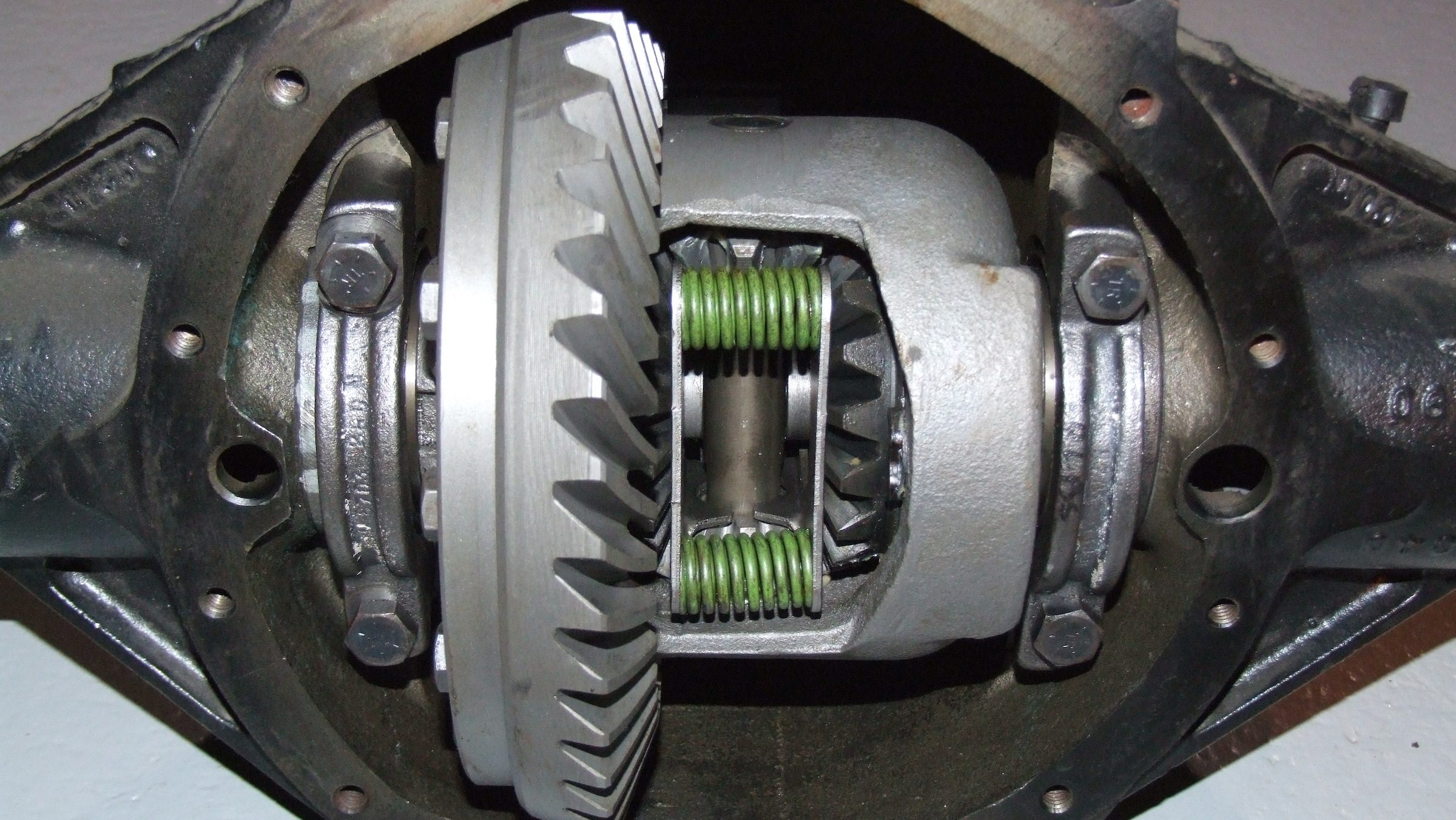
Are there different types of differential gears available?
Yes, there are different types of differential gears available, each designed to suit specific driving conditions and performance requirements. Here’s an overview of some commonly used types of differential gears:
1. Open Differential:
An open differential is the most basic and widely used type of differential gear. It allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns while equally distributing torque. In normal driving conditions, an open differential provides smooth operation and is relatively inexpensive. However, it has limited traction improvement capabilities and may distribute power to the wheel with the least resistance, which can be a disadvantage in low-traction situations.
2. Limited-Slip Differential (LSD):
A limited-slip differential (LSD) improves upon the capabilities of an open differential by providing some degree of torque biasing. LSDs use various mechanisms, such as clutch packs, viscous fluids, or gear arrangements, to transfer more torque to the wheel with better traction. This helps improve traction and power delivery, especially in situations where one wheel has reduced traction. LSDs strike a balance between improved traction and maintaining drivability for everyday use.
3. Electronic Limited-Slip Differential (ELSD):
An electronic limited-slip differential (ELSD) is a modern variation of the limited-slip differential. It incorporates electronic sensors and actuators to actively monitor wheel speeds and traction conditions. The ELSD can quickly and precisely distribute torque to the wheels with better traction, enhancing overall performance and stability. ELSDs are often found in high-performance or advanced all-wheel drive systems.
4. Torsen Differential:
A Torsen (short for Torque-Sensing) differential is a type of differential gear that uses a worm gear arrangement to distribute torque. Torsen differentials can provide a higher torque biasing ratio compared to LSDs. They have a mechanical, self-acting design that automatically transfers torque to the wheel with better traction. Torsen differentials are commonly used in performance-oriented vehicles and off-road applications.
5. Locking Differential:
A locking differential is designed to maximize traction in off-road or extreme driving conditions. It allows both wheels to receive an equal amount of torque simultaneously, regardless of traction conditions. Locking differentials can be manually engaged or automatically activated by sensors detecting wheel slip. While locking differentials enhance traction, they can also negatively impact handling on paved surfaces, making them more suitable for off-road or specialized applications.
6. Torque Vectoring Differential:
A torque vectoring differential is a more advanced type of differential that actively distributes torque to individual wheels to enhance vehicle dynamics. It uses electronic systems to monitor various vehicle parameters, such as wheel speed, steering input, and lateral acceleration. By selectively applying torque to specific wheels, torque vectoring differentials can improve cornering performance, stability, and agility.
These are just a few examples of the different types of differential gears available. Each type offers unique characteristics and advantages, allowing vehicle manufacturers to tailor the differential system to specific driving conditions, performance requirements, and driver preferences.


editor by CX 2024-03-01