Product Description
Gear technical data
| Product Type | M0.5~M12, Z8~80. standard gear, or according customer drawing to make. |
| Material: | Carbon Steel, Brass, Aluminium, Stainless steel, Plastic, POM, Delrin, Titanium Alloy etc. |
| Process method | CNC Turning, milling ,drilling, grinding etc. |
| Surface finish: | Chrome plating, Anodization, Powder coating, blackening, Sand blasting, Brushing & ploshing,Electrophoresis etc. |
| OEM & ODM Service | Available |
| Design Software | PRO/E, Auto CAD, Solid Works |
| Trade Terms: | FOB,,CIF,EXW |
| Payment Terms: | T/T, L/C, |
| Packing: | Foam, Carton, Standard Wooden boxes |
| Capacity | 8,000~1,5000 pcs per month |
| Delivery | 20-30 days after receiving PO |
| Applications | Automotive Parts,hydraulics, compressors,Industrial equipments, transmission parts, etc. |
| Our services: | CNC Machining, Milling, Stamping, Sheet metal fabricating, and Die-Casting |
Products show
Teeth cutting machining
Gear inspection
FAQ
Q: Are you trading company or manufacturer ?
A: We are factory.
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: Generally it is 5-10 days if the goods are in stock. or it is 15-20 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to quantity.
Q: Do you provide samples ? is it free or extra ?
A: Yes, we could offer the sample for free charge but do not pay the cost of freight.
Q: What is your terms of payment ?
A: Payment 30%TT in advance. 70% T/T before shippment
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | Internal Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Cut Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Cast Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 4/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
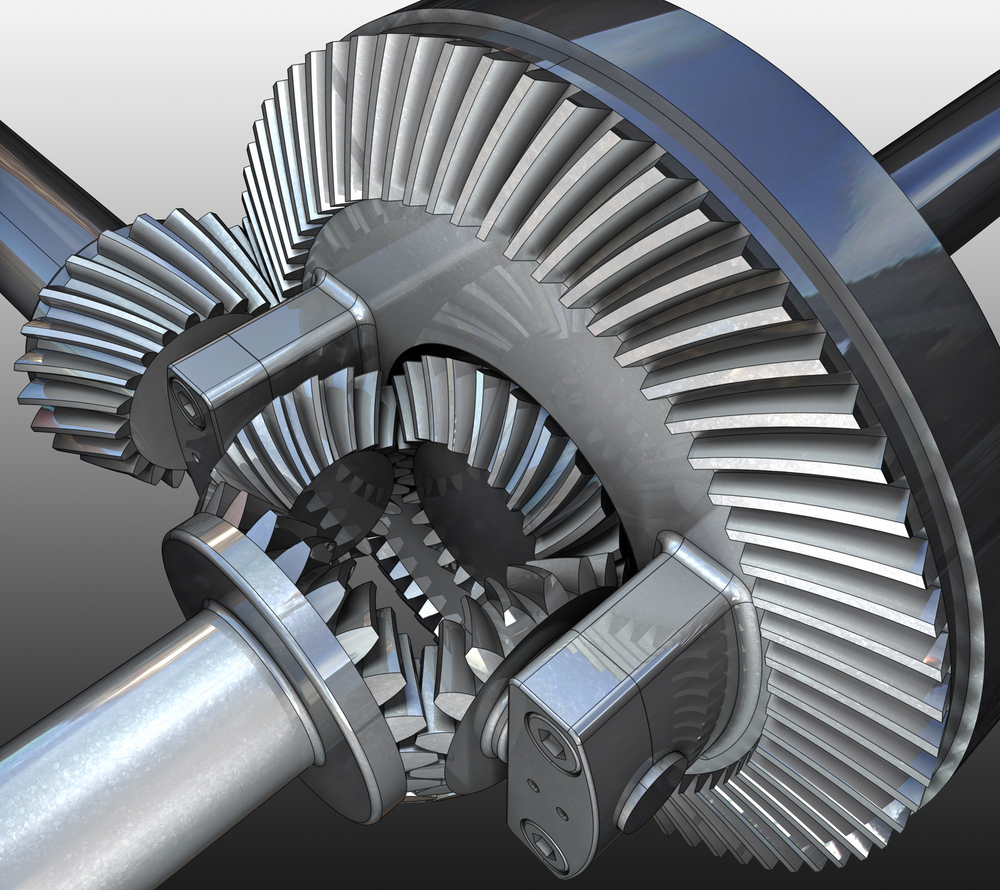
What is the impact of a malfunctioning differential gear on a vehicle’s performance?
A malfunctioning differential gear can significantly impact a vehicle’s performance and drivability. Here’s a detailed explanation of the effects of a malfunctioning differential gear:
1. Limited Traction:
A malfunctioning differential gear may result in limited traction, especially in off-road or slippery conditions. The differential gear distributes torque between the wheels to provide optimal traction. If the gear malfunctions, it may not distribute power evenly, causing one or more wheels to lose traction. This can result in wheel slip, difficulty in accelerating, and compromised control over the vehicle.
2. Poor Handling and Stability:
The differential gear plays a critical role in maintaining stability and handling characteristics of a vehicle. A malfunctioning differential gear can disrupt the balance between the wheels, leading to poor handling and stability. For example, if a rear-wheel-drive vehicle’s differential gear fails, it can cause excessive oversteer or understeer, making the vehicle difficult to control during cornering or sudden maneuvers.
3. Increased Tire Wear:
A malfunctioning differential gear can cause uneven tire wear. When the gear fails to distribute torque evenly, some wheels may experience excessive slippage or spinning, while others receive insufficient power. This uneven distribution of forces can lead to accelerated tire wear on specific wheels, resulting in uneven tread wear patterns and reducing the overall lifespan of the tires.
4. Abnormal Noise and Vibration:
A malfunctioning differential gear can produce abnormal noises and vibrations. If the gear’s components, such as bearings or gears, wear out or become damaged, it can result in grinding, whining, or clunking noises during operation. Additionally, the vehicle may experience vibrations, especially when accelerating or navigating turns. These symptoms indicate potential issues with the differential gear that require immediate attention.
5. Loss of Power and Performance:
A malfunctioning differential gear can lead to a loss of power and performance. If the gear fails to transfer torque effectively, the vehicle may experience reduced power delivery to the wheels. This can result in sluggish acceleration, decreased towing or hauling capacity, and overall compromised performance. The vehicle may struggle to climb inclines, navigate challenging terrain, or maintain speed efficiently.
6. Increased Fuel Consumption:
A malfunctioning differential gear can contribute to increased fuel consumption. When the gear fails to distribute torque properly, the engine may need to work harder to compensate for the lack of power transmission. This increased workload can lead to higher fuel consumption, as the engine consumes more fuel to maintain performance levels.
7. Safety Concerns:
A malfunctioning differential gear can pose safety concerns for the driver and passengers. Limited traction, poor handling, and compromised stability increase the risk of accidents, especially in adverse weather conditions or emergency situations. It is crucial to address any differential gear issues promptly to ensure the safe operation of the vehicle.
In summary, a malfunctioning differential gear can have a significant impact on a vehicle’s performance. It can result in limited traction, poor handling and stability, increased tire wear, abnormal noises and vibrations, loss of power and performance, increased fuel consumption, and safety concerns. Regular maintenance, prompt repairs, and addressing differential gear issues can help maintain the vehicle’s performance, drivability, and overall safety.
How do differential gears function in both front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles?
In both front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles, differential gears serve the same fundamental purpose of distributing power from the engine to the wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds. However, their specific configurations and functions differ between these two types of drivetrains. Here’s a detailed explanation of how differential gears function in both front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles:
Front-Wheel-Drive Vehicles:
In front-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are typically integrated into the transaxle assembly, which combines the transmission and differential into a single unit. Here’s how the differential gears function in front-wheel-drive vehicles:
- Power Input: The engine’s power is transmitted through the transmission to the transaxle assembly.
- Ring and Pinion Gears: The power from the transaxle is delivered to a set of ring and pinion gears within the differential assembly. These gears are responsible for distributing torque to the front wheels.
- Spider Gears: The ring gear is connected to a carrier that houses multiple smaller gears called spider gears. These spider gears allow the front wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns.
- Equal Torque Distribution: In front-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears prioritize equal torque distribution between the two front wheels. This design helps maintain traction and stability during acceleration and cornering.
- Traction Control: Some front-wheel-drive vehicles may also incorporate additional features in the differential assembly, such as electronic limited-slip differentials or traction control systems. These features help optimize traction by transferring power to the wheel with better grip, reducing wheel spin and improving overall performance.
Rear-Wheel-Drive Vehicles:
In rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are typically located in the rear axle assembly. Here’s how the differential gears function in rear-wheel-drive vehicles:
- Power Input: The engine’s power is transmitted through the transmission to the driveshaft, which connects to the rear axle assembly.
- Drive Pinion and Ring Gear: The driveshaft is connected to a drive pinion gear, which meshes with a larger ring gear. This gear set is responsible for transferring power to the rear wheels.
- Spider Gears: Similar to front-wheel-drive vehicles, rear-wheel-drive vehicles also have spider gears housed within the differential assembly. The spider gears allow the rear wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns.
- Torque Distribution: In rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears distribute torque to the rear wheels in a manner that prioritizes rear-wheel traction and propulsion. This configuration is particularly beneficial for vehicle acceleration and load-carrying capability.
- Enhanced Features: Rear-wheel-drive vehicles may also incorporate advanced differential systems, such as limited-slip differentials or electronic locking differentials, to optimize traction and performance. These features help improve grip, especially in challenging driving conditions or when driving off-road.
In summary, differential gears function differently in front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles due to their distinct drivetrain configurations. In front-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are typically integrated into the transaxle assembly and prioritize equal torque distribution to the front wheels. In rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are located in the rear axle assembly and focus on torque distribution to the rear wheels for propulsion. Understanding the specific functions of differential gears in each drivetrain type is essential for optimizing vehicle performance, traction, and stability.
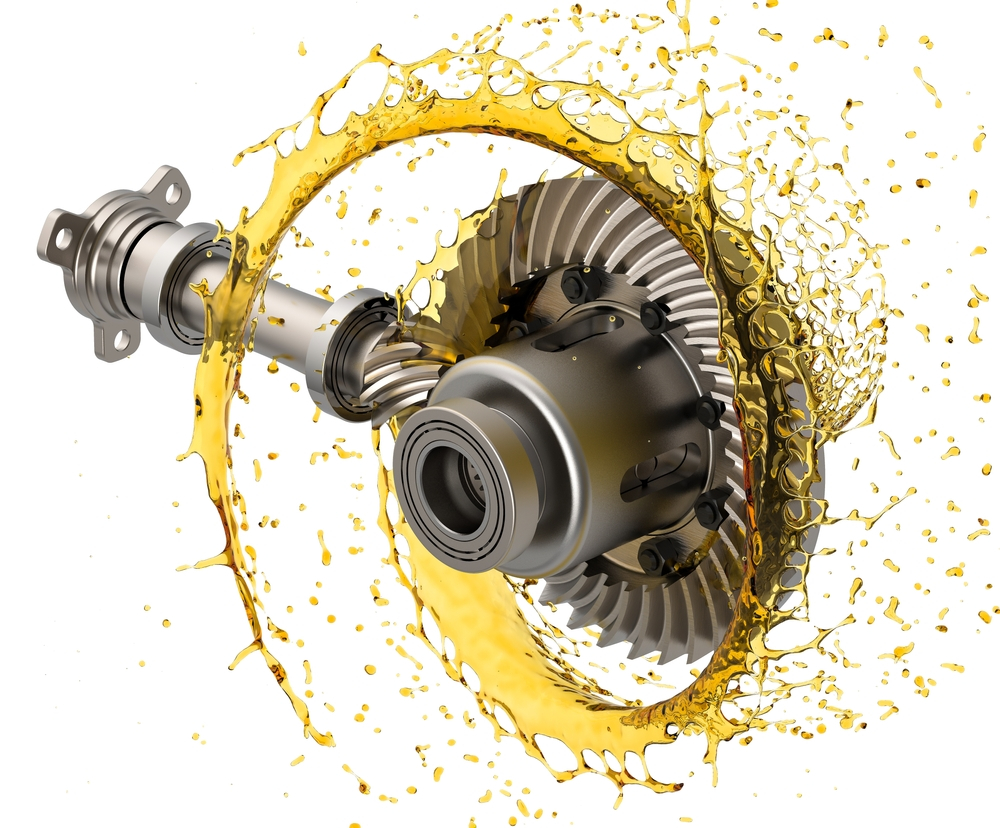

Can you explain the concept of torque distribution in a differential gear?
Torque distribution is a fundamental concept in a differential gear that refers to the way rotational force is distributed among the wheels of a vehicle. Here’s a detailed explanation:
In a vehicle equipped with a differential gear, torque is transmitted from the engine to the differential, and then further distributed to the wheels. The differential gear ensures that torque is divided between the wheels, allowing them to receive power and propel the vehicle forward.
1. Power Input:
The torque distribution process begins with the power input from the engine. The engine generates rotational force, or torque, which is transmitted through the drivetrain to the differential gear.
2. Differential Assembly:
Within the differential gear, torque is distributed among several components, including the ring gear, pinion gear, side gears, and spider gears. The specific arrangement may differ depending on the type of differential used.
3. Side Gears and Spider Gears:
The side gears are connected to the axle shafts, which extend to the wheels. The spider gears, also known as planetary gears, are positioned between the side gears. When torque is applied to the differential assembly, it is transferred to the side gears through the spider gears.
4. Equal Torque Distribution:
In a straight-line driving scenario, where both wheels have equal traction and are rotating at the same speed, the spider gears rotate freely on their respective shafts. This allows the side gears to rotate at the same speed as the differential case, resulting in equal torque distribution to both wheels. As a result, both wheels receive an equal share of power from the differential.
5. Unequal Torque Distribution:
During turns or when one wheel encounters different traction conditions, the wheels need to rotate at different speeds. In this situation, the spider gears are forced to rotate along with the side gears due to the difference in rotational speeds between the two wheels.
As the spider gears rotate, they allow the side gears to rotate at different speeds, compensating for the variation in wheel speeds. This results in unequal torque distribution, with the outer wheel (on the outside of the turn) receiving more torque and the inner wheel (on the inside of the turn) receiving less torque. The differential gear enables this torque differentiation, ensuring that the wheels can rotate independently while still receiving power from the differential.
6. Optimizing Traction:
The torque distribution in a differential gear plays a crucial role in optimizing traction. Unequal torque distribution allows the wheel with better traction to receive more power, maximizing the vehicle’s ability to maintain forward motion. This is particularly beneficial in situations where one wheel is on a slippery surface or encounters reduced traction conditions.
7. Differential Types:
It’s important to note that different types of differentials can provide varying torque distribution characteristics. For example, open differentials primarily distribute torque equally, while limited-slip differentials and locking differentials offer varying degrees of torque biasing to improve traction in specific conditions.
In summary, torque distribution in a differential gear refers to the division of rotational force among the wheels of a vehicle. The differential gear enables equal torque distribution during straight-line driving and unequal torque distribution during turns or varied traction conditions. By optimizing torque distribution, the differential gear ensures efficient power delivery, traction optimization, and overall performance of the vehicle.


editor by CX 2023-11-29