Product Description
Key attributes
Other attributes
Applicable Industries
Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Repair Shops, Food & Beverage Factory, Retail, Construction works , Energy & Mining, Other
Weight (KG)
1200
Showroom Location
None
Video outgoing-inspection
Provided
Machinery Test Report
Provided
Marketing Type
New Product 2571
Warranty of core components
1 Year
Core Components
Gear
Place of CHINAMFG
ZheJiang , China
Condition
New
Warranty
1.5 years
Shape
Spur
Brand Name
TS
Material
Steel
Product Name
Large Diameter Ring Gears
Process
Milling,hobbing
Surface treatment
Grinding
Heat treatment
Q&T
Application
Industry machinery,transmission equipment
Standard
DIN ANSI ISO
Certificate
ISO 9001:2015
Module No.
Customized
Size
Customer’s Drawing
Quality
High level
Packaging and delivery
Packaging Details
Package adapting to CHINAMFG transport
Port
HangZhou, ZheJiang
Supply Ability
Supply Ability
15 Piece/Pieces per Month steel large spur gears
OUR WORKSHOPS
OUR EQUIPMENTS
Technology Process
|
Material |
Carbon steel,Alloy steel |
||
|
Structure |
Forging,casting |
||
|
Type of gear |
spur gear,helical gear,Planetary Gear |
||
|
Heat treatment |
Quenching and tempering |
||
|
Process |
forging, rough machining, QT, finish machining |
||
|
Main equipments |
hobbing,CNC machine |
||
|
Module |
up to 200 |
||
|
Precision of gear |
Grinding ISO Grade 5-7 & Hobbing ISO Grade 8-9 |
||
|
Inspection |
Raw material inspection, UT,physical property test,dimension inspect |
||
|
Application |
Mining machinery, mill, kiln and other equipment |
||
OUR CERTIFICATE
OUR CUSTOMER FEEDBACK
CONTACT
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industry |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hb190-Hb300 |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
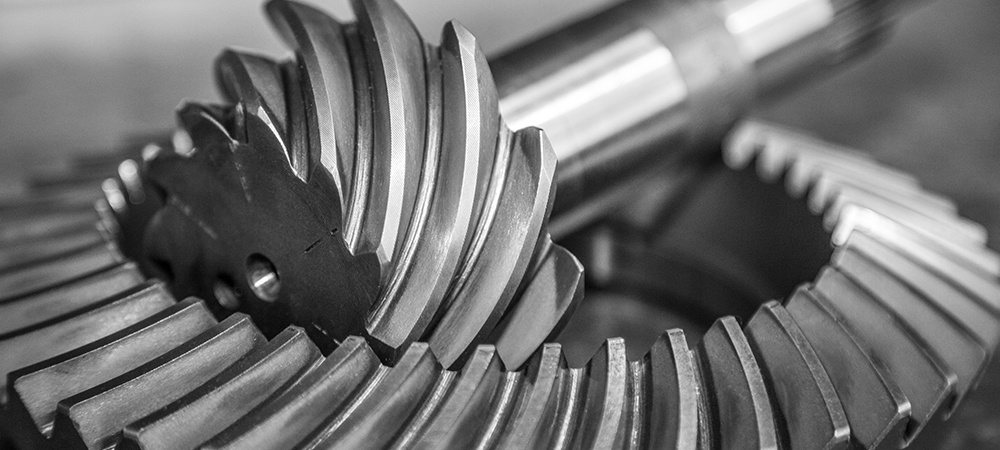

How do ring gears contribute to power transmission?
Ring gears play a significant role in power transmission within mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how ring gears contribute to power transmission:
- Torque Transfer: Ring gears are designed with teeth on their outer or inner circumference, depending on whether they are external or internal ring gears. These teeth mesh with the teeth of other gears, such as pinion gears or planetary gears. As the driving gear rotates, the meshing teeth engage with the ring gear’s teeth, transmitting torque from the driving gear to the ring gear. This torque transfer enables the ring gear to rotate and transmit power to other components or systems connected to it.
- Rotational Motion: Ring gears convert the rotational motion of the driving gear into rotational motion of the ring gear itself. The teeth on the ring gear provide a positive engagement with the teeth of the driving gear, ensuring a synchronized rotation. As the driving gear rotates, the meshing teeth push against the ring gear’s teeth, causing it to rotate in the same direction and at a proportional speed determined by the gear ratio. This rotational motion is crucial for transmitting power to different parts of the system or driving various mechanisms and components.
- Speed Reduction or Increase: Ring gears, in conjunction with other gears in the system, can be used to achieve speed reduction or increase. By varying the sizes of the driving gear, the ring gear, and other intermediate gears, different gear ratios can be achieved. When the driving gear is smaller than the ring gear, the ring gear rotates at a slower speed than the driving gear, resulting in speed reduction. Conversely, if the driving gear is larger, the ring gear rotates at a faster speed, leading to speed increase. This ability to control gear ratios allows for power transmission at desired speeds and enables systems to meet specific operational requirements.
- Load Distribution: Ring gears distribute the transmitted loads across their circumference. The teeth of the ring gear engage with multiple teeth of other gears, ensuring that the load is shared among these meshing points. This load distribution helps prevent localized stress concentrations and excessive wear on specific gear teeth. By distributing the load, ring gears contribute to the overall durability and longevity of the gear system, allowing for reliable power transmission even under demanding conditions.
- Compact and Efficient Design: Ring gears offer a compact and efficient design for power transmission. Their annular shape allows for a high gear ratio within a small space, making them ideal for applications where space is limited. Additionally, ring gears can be integrated into various gear configurations, such as planetary gear systems or gearboxes, which further enhance their power transmission capabilities. This compact and efficient design contributes to overall system efficiency and performance.
Overall, ring gears are essential components in power transmission systems. Through torque transfer, rotational motion, speed control, load distribution, and their compact design, ring gears enable efficient and reliable power transmission in a wide range of mechanical applications.

Are ring gears suitable for high-torque applications?
Ring gears are indeed suitable for high-torque applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of why ring gears are suitable for high-torque applications:
Ring gears are designed to handle high torque loads and are commonly used in various applications that require substantial torque transmission. Here are the reasons why ring gears are well-suited for high-torque applications:
- Robust Construction: Ring gears are typically constructed with robust materials, such as hardened steel or other high-strength alloys. This construction provides the necessary strength, durability, and resistance to withstand high torque forces without deformation or failure.
- Large Contact Area: Ring gears have a large contact area between their gear teeth, which allows for efficient power transmission and load distribution. The larger contact area enables the ring gear to transmit higher torque without experiencing excessive stress concentrations or localized overloading.
- Optimized Tooth Geometry: The tooth geometry of ring gears is designed to handle high torque. The shape and profile of the gear teeth are optimized to distribute the torque load evenly, minimizing stress concentrations and enhancing the gear’s ability to transmit higher torque without premature wear or failure.
- Multiple Gear Engagements: Ring gears often engage with multiple gears or pinions, which further enhances their torque capacity. The engagement of multiple gears allows for load sharing, distributing the torque across multiple contact points and reducing the strain on individual gear teeth.
- Customizable Gear Ratios: Ring gears can be designed with various gear ratios to meet specific torque requirements. By adjusting the tooth count or diameter of the ring gear and mating gears, the gear system can be optimized for high torque applications while maintaining the desired speed or rotational characteristics.
- Used in Heavy-Duty Applications: Ring gears are widely used in heavy-duty applications that demand high torque transmission. Examples include automotive differentials, industrial gearboxes, mining equipment, construction machinery, and wind turbines. These applications rely on ring gears to effectively transmit and handle the high torque generated by powerful engines, motors, or turbines.
It’s important to note that while ring gears are suitable for high-torque applications, proper engineering analysis and selection should be carried out to ensure that the specific design, material, and size of the ring gear are appropriate for the intended torque requirements. Factors such as gear tooth strength, gear geometry, material properties, lubrication, and operating conditions should be carefully considered to ensure reliable and efficient performance in high-torque applications.
What are the applications of ring gears?
Ring gears, also known as annular gears or internal gears, have a wide range of applications across various industries and mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of the applications of ring gears:
Ring gears are commonly used in numerous applications where rotational motion, torque transmission, and load distribution are essential. The unique design and characteristics of ring gears make them suitable for a variety of mechanical systems. Here are some common applications of ring gears:
- Automotive Transmissions: Ring gears are extensively used in automotive transmissions, particularly in automatic and manual transmissions. They are part of the gear train that transfers rotational motion and torque from the engine to the wheels. Ring gears in automotive applications are typically large in size and designed to handle high torque loads.
- Differential Systems: Ring gears play a crucial role in differential systems found in vehicles. The differential assembly allows the wheels on an axle to rotate at different speeds while distributing torque evenly. Ring gears form an integral part of the differential assembly, enabling torque transfer and speed differentiation between the drive wheels.
- Planetary Gear Systems: Ring gears are a fundamental component in planetary gear systems, which are widely used in various applications. Planetary gear systems consist of a central sun gear, planet gears, and a ring gear. The ring gear serves as the outer ring that meshes with the planet gears and the sun gear. Planetary gear systems offer high gear ratios, compactness, and versatility, making them suitable for applications such as automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, and aerospace systems.
- Industrial Machinery: Ring gears find extensive use in industrial machinery for power transmission, motion control, and speed regulation. They are employed in equipment such as gearboxes, speed reducers, hoists, conveyors, and rotary tables. Ring gears enable efficient torque transmission, precise motion control, and load distribution in these industrial applications.
- Robotics and Automation: Ring gears are utilized in robotics and automation systems for precise motion control and synchronization. They can be found in robotic arms, automated assembly lines, CNC machines, and other robotic applications where accurate positioning and precise motion are critical. Ring gears provide the necessary torque transmission and gear reduction required for precise robotic movements.
- Power Generation: Ring gears are used in power generation equipment, such as wind turbines and hydroelectric generators. They form part of the gearboxes that convert the rotational motion of the turbine or generator rotor into electrical energy. Ring gears in power generation applications need to handle high torque loads, operate reliably, and provide efficient power transmission.
- Heavy Machinery and Construction Equipment: Ring gears are employed in heavy machinery and construction equipment, including excavators, cranes, mining equipment, and agricultural machinery. They facilitate the transmission of power and torque for various functions, such as lifting, digging, and material handling. Ring gears in these applications are designed to withstand high loads, rugged environments, and demanding operating conditions.
These are just a few examples of the applications of ring gears. Their versatility, load-carrying capacity, compact design, and ability to achieve high gear ratios make them suitable for a wide range of mechanical systems across industries.
The specific design, size, and material selection of ring gears may vary depending on the application requirements, operating conditions, and performance specifications.


editor by Dream 2024-05-14
China Custom Auto Spare Parts Differential Gear for Japanese Trucks Hino 41341-1150 gear box
Product Description
Product Description
| Gear model | Customized gear accoding to customers sample or drawing |
| product name | Customized Bevel Gear for Reducer/ Oil Drilling Rig/ Construction Machinery/ Truck |
| material | stainless steel , iron , aluminum ,bronze ,carbon steel ,brass , nylon etc . |
| N.W | 4.5KG |
| BORE | Finished bore, Pilot Bore, Special request |
| surface treatment | Carburizing and Quenching,Tempering ,Tooth suface high quenching Hardening,Tempering |
| Processing Method | Molding, Shaving, Hobbing, Drilling, Tapping, Reaming, Manual Chamfering, Grinding etc |
| Heat Treatment | Quenching & Tempering, Carburizing & Quenching, High-frequency Hardening, Carbonitriding…… |
| Package | Wooden Case/Container and pallet, or made-to-order |
| Certificate | ISO9001 TS16949 |
| Machining Process | Gear Hobbing, Gear Milling, Gear Shaping, Gear Broaching, Gear Shaving, Gear Grinding and Gear Lapping ,gear accuracy testing |
| OEM: | 41341-1150 |
Detailed Photos
Certifications
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
ZheJiang Province Tonging Automobile Synchronizer Co., Ltd and ZheJiang HangZhou Xihu (West Lake) Dis.g Gears Co. Ltd are focus on the production of space parts for the CHINAMFG over 35years. a professional company in the field.
Our spare parts are interchangeable with the major manufacturers of heavy duty trucks, buses, light commercial and 4×4 pick up vehicles, medium and heavy duty Japanese applications. New items developing for customized in earthmover and agriculture machines.
There are 1 forging production line of 1600 tons, several forging
production lines from 400 tons to 1000 tons: more than 300 various
manufacturing and inspecting equipments with high efficiency and
precision; 2 heat treatment production lines.
FAQ
| Q1. What is your terms of packing? |
| A: Generally, we pack our goods in Crates/Pallet/Boxes/Cartons. |
| Q2. How about your delivery time? |
| A: Generally, it is 3-7days if the goods are in stock,or it is need 30-60days to producing,it is according to the quantity. |
| Q3. Can you produce according to the samples? |
| A: Yes, we can produce by your samples or technical drawings. We can build the molds and fixtures. |
| Q4. Do you test all your goods before delivery? |
| A: Yes, we have 100% test before delivery |
| Q5.Do you provide samples?is it free or extra? |
| A:yes,We receive 30% of the order and can provide samples free of charge,but do not pay the cost of freight. |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Type: | Differential Bearing |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
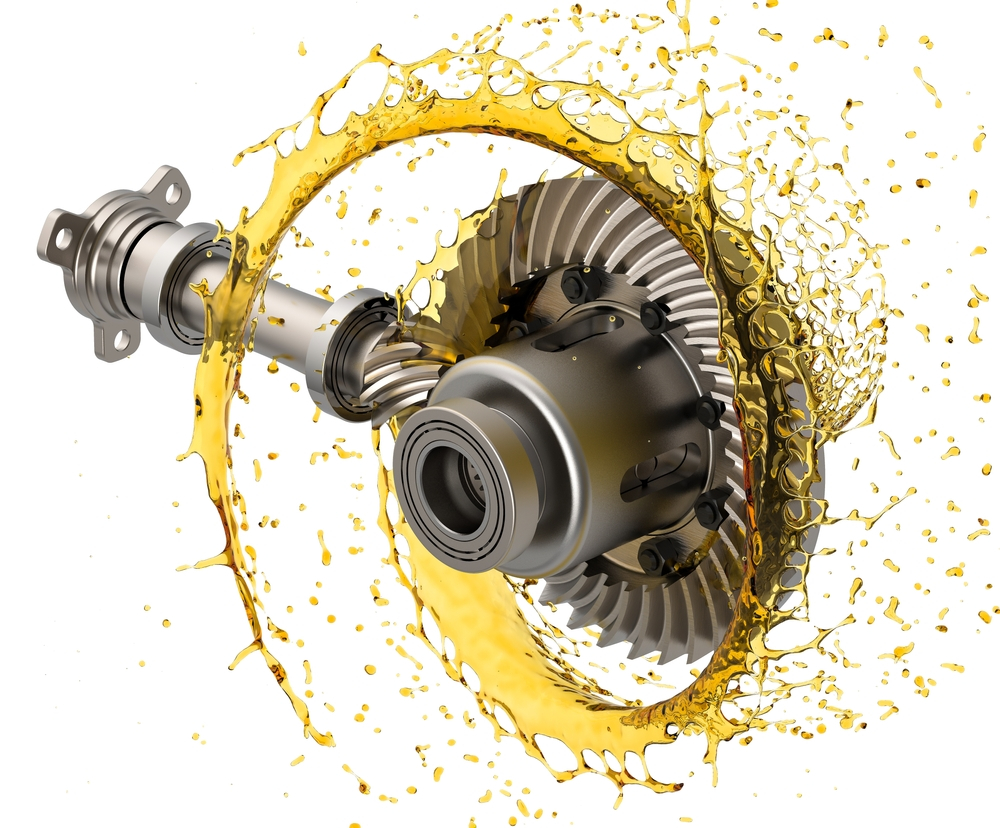

How does a differential gear distribute power between the wheels?
A differential gear is responsible for distributing power between the wheels of a vehicle, allowing them to rotate at different speeds while maintaining torque transfer. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a differential gear accomplishes this:
1. Power Input:
The differential gear receives power from the transmission or driveshaft connected to the engine. This power is transmitted to the differential assembly, which is typically located in the axle housing.
2. Ring and Pinion Gears:
Within the differential assembly, the power from the driveshaft is transferred to the ring and pinion gears. The ring gear is a large gear that surrounds the differential assembly, while the pinion gear is a smaller gear connected to the driveshaft. The interaction between these gears allows the power to be redirected.
3. Side Gears and Spider Gears:
The ring gear is connected to side gears, also known as bevel gears, through a set of small gears called spider gears. The side gears are attached to the axle shafts, which are responsible for transmitting power to the wheels. The spider gears allow the side gears to rotate independently of each other while maintaining torque transfer.
4. Differential Action:
As the vehicle moves, the differential gears enable the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns. When the vehicle is moving in a straight line, the spider gears rotate smoothly, allowing equal power distribution to both wheels. However, during a turn, the inside wheel travels a shorter distance than the outside wheel, causing them to rotate at different speeds.
5. Speed and Torque Distribution:
The differential gear adjusts the speed and torque distribution between the wheels based on their rotational differences. When the vehicle is turning, the spider gears allow one wheel to rotate faster than the other, ensuring that torque is transferred to the wheel with better traction. This allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds, preventing tire scrubbing and providing smooth cornering.
6. Limited-Slip and Locking Differentials:
In certain differential systems, such as limited-slip differentials or locking differentials, additional mechanisms are incorporated to enhance traction and power distribution. Limited-slip differentials use clutch packs or friction plates to provide a predetermined amount of resistance, allowing some speed differentiation between the wheels while still transferring power. Locking differentials, on the other hand, lock the side gears together, ensuring equal torque distribution to both wheels, regardless of traction conditions.
7. Differential Types:
There are various types of differentials, including open differentials, limited-slip differentials, electronic differentials, torque vectoring differentials, and more. Each type has its own mechanisms and technologies to distribute power between the wheels effectively, depending on the vehicle’s requirements and driving conditions.
In summary, a differential gear distributes power between the wheels by utilizing a system of gears, including ring and pinion gears, side gears, and spider gears. The differential action allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns, ensuring smooth cornering and preventing tire scrubbing. Additional mechanisms, such as limited-slip or locking differentials, can further enhance traction and power distribution in various driving conditions.
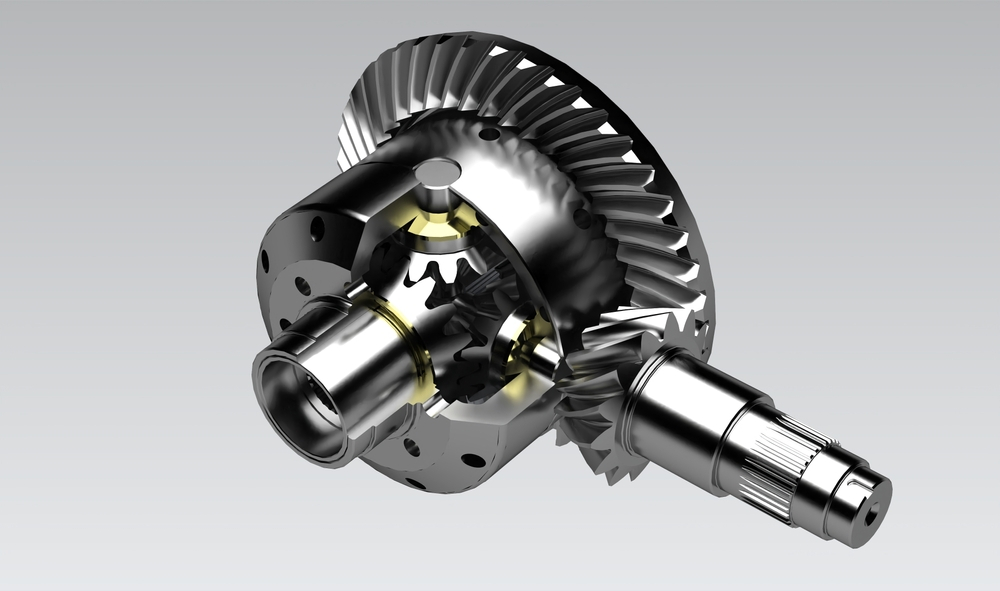
What are the considerations for choosing the right type of differential gear for a vehicle?
When selecting the appropriate type of differential gear for a vehicle, several considerations come into play. Choosing the right differential gear involves assessing factors such as vehicle characteristics, intended use, driving conditions, and desired performance. Here’s a detailed explanation of the considerations for choosing the right type of differential gear:
- Vehicle Type: The type of vehicle, whether it’s a passenger car, SUV, truck, or performance vehicle, plays a significant role in determining the appropriate differential gear. Different types of vehicles have varying weight distributions, power outputs, and handling characteristics, which influence the optimal choice of differential gear.
- Driving Conditions: The intended driving conditions are crucial in selecting the right differential gear. Factors such as road surface, weather conditions, and terrain should be considered. For example, vehicles driven primarily on paved roads may benefit from different differential gear options compared to off-road vehicles that frequently encounter challenging terrain or vehicles that operate in regions with snowy or icy conditions.
- Performance Requirements: The desired performance attributes of the vehicle are important considerations. Some drivers prioritize acceleration and high-speed performance, while others focus on off-road capabilities, towing capacity, or fuel efficiency. Differential gears can be chosen to optimize specific performance aspects, such as maximizing traction, improving handling, enhancing torque delivery, or achieving better fuel economy.
- Traction Needs: The level of traction required is a key factor in selecting the right differential gear. Vehicles that need maximum traction in challenging conditions, such as racing cars, off-road vehicles, or vehicles used in low-grip environments, may benefit from limited-slip differentials or locking differentials. These differential types help distribute power to the wheels with the most grip, enhancing traction and maintaining vehicle control.
- Driving Dynamics: The desired driving dynamics and handling characteristics also influence the choice of differential gear. Some drivers prefer a more predictable and balanced handling, while others may desire more aggressive cornering capabilities. Differential gears with specific characteristics, such as torque vectoring differentials, can enhance these driving dynamics by actively managing torque distribution between individual wheels.
- Budget: Cost considerations are also significant when choosing a differential gear. Different types of differential gears vary in terms of complexity, features, and pricing. It’s essential to evaluate the budget constraints and weigh the cost against the desired performance benefits and requirements.
In summary, selecting the right type of differential gear for a vehicle involves considering factors such as vehicle type, driving conditions, performance requirements, traction needs, driving dynamics, and budget. By carefully assessing these considerations, drivers can choose a differential gear that aligns with their vehicle’s characteristics, intended use, and performance objectives, ultimately enhancing traction, handling, and overall driving experience.
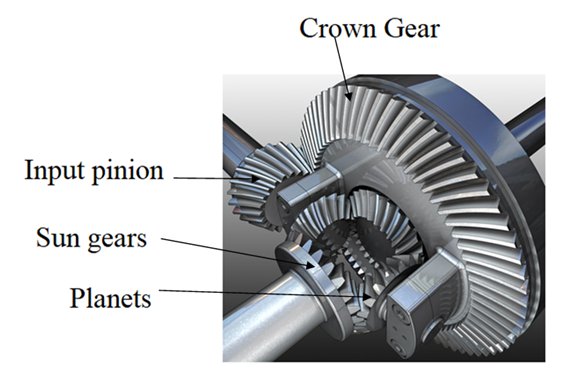
What are the applications of differential gears in off-road vehicles?
Off-road vehicles rely on differential gears for various applications that enhance their performance and capability in challenging terrains. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Traction Improvement:
One of the primary applications of differential gears in off-road vehicles is to improve traction. Off-road terrain often consists of uneven surfaces, loose soil, rocks, mud, or deep snow, which can cause the wheels to lose traction. Differential gears, such as limited-slip differentials or locking differentials, help distribute torque to the wheels with better traction, reducing wheel slip and maximizing grip. This allows off-road vehicles to maintain forward momentum and conquer obstacles that would otherwise be difficult to navigate.
2. All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Systems:
Off-road vehicles commonly utilize differential gears in their all-wheel drive (AWD) systems. AWD systems distribute power to all four wheels, providing better traction and stability on off-road terrain. Differential gears enable power transfer between the front and rear axles, as well as between the left and right wheels on each axle, allowing for optimal torque distribution based on traction conditions. This helps improve overall off-road performance and control.
3. Articulation and Wheel Independence:
Off-road vehicles often encounter uneven terrain with varying degrees of wheel articulation. Differential gears play a crucial role in maintaining wheel independence, allowing each wheel to move up or down independently to better conform to the terrain. This ensures that the wheels maintain contact with the ground and enhances traction, especially when navigating over rocks, logs, or steep inclines.
4. Hill Climbing and Descending:
When climbing steep inclines or descending steep slopes, differential gears are essential for off-road vehicles. In these situations, differential gears help distribute torque between the wheels on each axle, allowing the wheels with better traction to propel the vehicle forward or provide controlled braking. This improves stability, prevents wheel slip, and enhances the vehicle’s ability to tackle challenging uphill or downhill sections.
5. Off-Road Racing:
In off-road racing, differential gears are utilized to optimize performance and handling. High-performance off-road vehicles often employ advanced differential systems, such as limited-slip differentials or torque vectoring differentials. These systems actively distribute torque to the wheels with better traction, improving acceleration, cornering ability, and overall vehicle dynamics in competitive off-road racing environments.
6. Rock Crawling and Trail Driving:
Off-road vehicles designed for rock crawling or trail driving heavily rely on differential gears. These vehicles require precise control and maximum traction in low-speed, technical situations. Differential gears, particularly locking differentials, are employed to ensure that both wheels on an axle rotate together, maximizing traction and allowing the vehicle to maneuver over challenging obstacles, such as large rocks, boulders, or deep ruts.
In summary, differential gears in off-road vehicles have several applications, including traction improvement, all-wheel drive systems, articulation and wheel independence, hill climbing and descending, off-road racing, rock crawling, and trail driving. These applications enhance the performance, control, and capability of off-road vehicles in demanding and rugged terrains.


editor by Dream 2024-05-14
China Custom Brand New Auto Rear CZPT and Pinion Gears for CZPT Hiace Hilux gear box
Product Description
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
| Brand New Auto Rear CHINAMFG And Pinion Gears For CHINAMFG hiace hilux | ||||||
| Compose | Differential case,Differential flange part,Crown and pinion,Small differential,Bearings | |||||
| Car make | For Hiace Hilux | |||||
| Speed ratio | 8*39 9*41 10*41 10*43 11*43 12*43 | |||||
| Pinion length | 215mm | |||||
| Ring gear inner diameter | 126mm | |||||
| Ring gear outer diameter | 204mm | |||||
| Material (housing) | Nodular cast iron | |||||
| Material (gears) | 20CrMnTiH3 | |||||
| Alex spline teeth | 30T | |||||
New models are welcome if samples or technical drawings can be supplied.
★Advantage 1 Good-quality material used to manufacture high-class products, much better than our archrivals.
★Advantage 2 Rough machining, fine machining, heat treatment, grinding, polishing, rust prevention, etc. Different processes have different functions.
★Advantage 3 Tolerance of products is no more than 0.01%, as the result of metallographic phase test, noise test, and other strict measurements.
ABOUT US
HangZhou CHINAMFG Imp.& Exp.Co .,Ltd located in HangZhou,ZHangZhoug Province. Have been committed to developing & supplying Auto Transmission Parts,putting ourselves to clients’ shoes to solve their demands.our company is mainly engaged in Auto Transmission Parts such as Transmission gearbox,Gear haft,Synchronizer ring,Cylinder
Head and Differcial Assembly and so on.
With our honesty and credit, we sincerely hope to cooperate with you for greater development. Welcome new and old customers from all walks of life to contact us for future business relationships and achieving mutual success!
RELATED PRODUCT
Generally, we pack our goods in neutral white boxes and brown cartons. If you have legally registered patent,
we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
CONTACT
FAQ
★ What is your terms of packing?
A: Generally, we pack our goods in neutral white boxes and brown cartons. If you have legally registered patent,
we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
★ What is your terms of payment?
A: T/T 30% as deposit, and 70% before delivery. We’ll show you the photos of the products and packages
before you pay the balance.
★Can you produce according to the samples?
A: Yes, we can produce by your samples or technical drawings. We can build the molds and fixtures.
Action now contact us for whole CATALOG.
MORE THEN 2000 KINDS OF OEM PARTS WAITTING FOR YHOU. PLEASE CONTACT US THE WHOLE CATALOG.
TRUST YOU WILL LIKE OUR DESIGNS & PRICE.
Please contat us for the WHOLE CATALOG. More than 2000 OEM PARTS.
WAITTING FOR YOU !!
ACTION NOW
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Differential |
|---|---|
| Material: | 20crmntih3 |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Automatic: | Manual |
| Standard: | Standard |
| Condition: | New |
| Samples: |
US$ 180/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do differential gears handle varying speeds in a vehicle’s wheels?
A differential gear system is designed to handle varying speeds in a vehicle’s wheels, allowing them to rotate at different rates while maintaining torque distribution. Here’s a detailed explanation of how differential gears achieve this:
1. Differential Assembly:
The differential assembly consists of several gears, including the ring and pinion gears, side gears, and spider gears. These components work together to accommodate varying speeds between the wheels.
2. Power Input:
The power is delivered to the differential gears through the driveshaft or transmission. The ring gear receives this power from the driveshaft, while the pinion gear is connected to the ring gear and transfers the rotational force to the differential assembly.
3. Speed Differences:
When a vehicle is moving in a straight line, the wheels ideally rotate at the same speed. However, during turns or when encountering different traction conditions, the wheels need to rotate at varying speeds. This is because the wheel on the outside of a turn covers a greater distance than the inside wheel, resulting in a speed differential.
4. Spider Gears:
The differential gears utilize spider gears, which are small gears located between the side gears. Spider gears allow the side gears to rotate independently of each other, accommodating the speed differences between the wheels.
5. Torque Distribution:
As the spider gears allow the side gears to rotate independently, torque is distributed between the wheels based on their speed differences. The wheel with less resistance or greater traction receives more torque, while the wheel with more resistance or lower traction receives less torque.
6. Smooth Cornering:
During turns, the inside wheel needs to rotate at a slower speed than the outside wheel. The differential gears allow this speed differentiation, enabling smooth cornering without wheel hop or tire scrubbing. By distributing torque appropriately, the differential gears ensure that both wheels receive sufficient power for optimal traction and control.
7. Limited-Slip and Locking Differentials:
In certain differential systems, such as limited-slip differentials or locking differentials, additional mechanisms are employed to further regulate speed differences and torque distribution. Limited-slip differentials use clutch packs or friction plates to provide a predetermined amount of resistance, allowing some differentiation between the wheels while still transferring power. Locking differentials lock the side gears together, ensuring equal torque distribution to both wheels, regardless of traction conditions.
8. Differential Types:
There are different types of differentials, including open differentials, limited-slip differentials, electronic differentials, torque vectoring differentials, and more. Each type utilizes specific technologies and mechanisms to handle varying speeds and torque distribution based on the vehicle’s requirements and driving conditions.
In summary, differential gears handle varying speeds in a vehicle’s wheels by utilizing a system of gears, including spider gears, side gears, ring and pinion gears. The speed differences between the wheels are accommodated by allowing independent rotation of the side gears through the spider gears. Torque distribution is adjusted to ensure optimal traction and control during turns and varying traction conditions. Additional mechanisms, such as limited-slip or locking differentials, can further regulate speed differences and torque distribution for enhanced performance and stability.
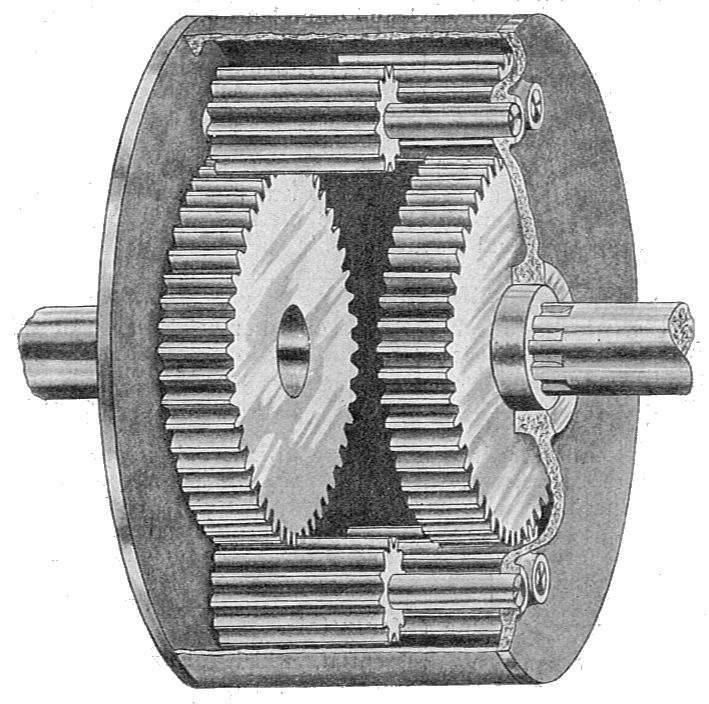
How do differential gears function in both front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles?
In both front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles, differential gears serve the same fundamental purpose of distributing power from the engine to the wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds. However, their specific configurations and functions differ between these two types of drivetrains. Here’s a detailed explanation of how differential gears function in both front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles:
Front-Wheel-Drive Vehicles:
In front-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are typically integrated into the transaxle assembly, which combines the transmission and differential into a single unit. Here’s how the differential gears function in front-wheel-drive vehicles:
- Power Input: The engine’s power is transmitted through the transmission to the transaxle assembly.
- Ring and Pinion Gears: The power from the transaxle is delivered to a set of ring and pinion gears within the differential assembly. These gears are responsible for distributing torque to the front wheels.
- Spider Gears: The ring gear is connected to a carrier that houses multiple smaller gears called spider gears. These spider gears allow the front wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns.
- Equal Torque Distribution: In front-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears prioritize equal torque distribution between the two front wheels. This design helps maintain traction and stability during acceleration and cornering.
- Traction Control: Some front-wheel-drive vehicles may also incorporate additional features in the differential assembly, such as electronic limited-slip differentials or traction control systems. These features help optimize traction by transferring power to the wheel with better grip, reducing wheel spin and improving overall performance.
Rear-Wheel-Drive Vehicles:
In rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are typically located in the rear axle assembly. Here’s how the differential gears function in rear-wheel-drive vehicles:
- Power Input: The engine’s power is transmitted through the transmission to the driveshaft, which connects to the rear axle assembly.
- Drive Pinion and Ring Gear: The driveshaft is connected to a drive pinion gear, which meshes with a larger ring gear. This gear set is responsible for transferring power to the rear wheels.
- Spider Gears: Similar to front-wheel-drive vehicles, rear-wheel-drive vehicles also have spider gears housed within the differential assembly. The spider gears allow the rear wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns.
- Torque Distribution: In rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears distribute torque to the rear wheels in a manner that prioritizes rear-wheel traction and propulsion. This configuration is particularly beneficial for vehicle acceleration and load-carrying capability.
- Enhanced Features: Rear-wheel-drive vehicles may also incorporate advanced differential systems, such as limited-slip differentials or electronic locking differentials, to optimize traction and performance. These features help improve grip, especially in challenging driving conditions or when driving off-road.
In summary, differential gears function differently in front-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles due to their distinct drivetrain configurations. In front-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are typically integrated into the transaxle assembly and prioritize equal torque distribution to the front wheels. In rear-wheel-drive vehicles, the differential gears are located in the rear axle assembly and focus on torque distribution to the rear wheels for propulsion. Understanding the specific functions of differential gears in each drivetrain type is essential for optimizing vehicle performance, traction, and stability.
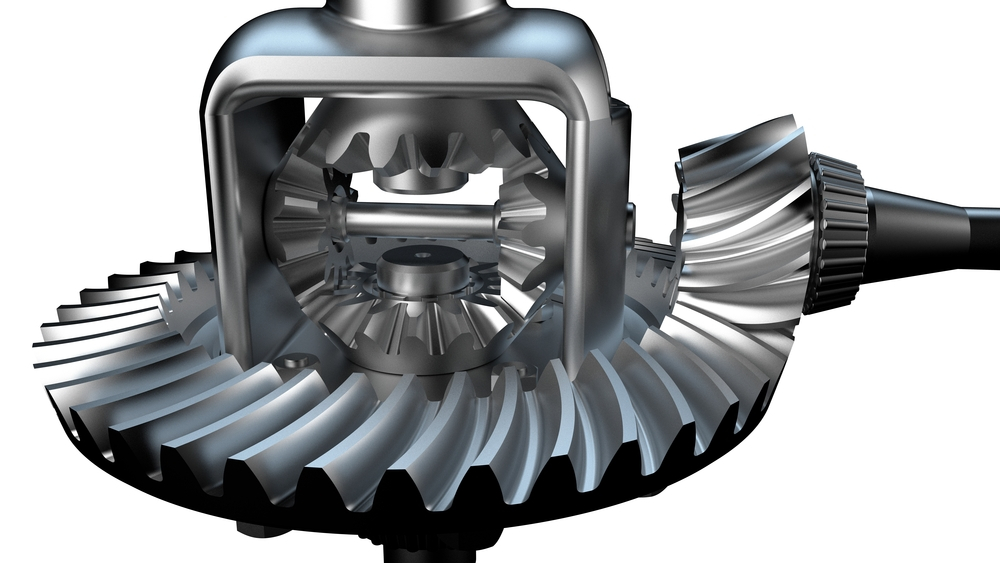
How do differential gears contribute to handling and stability in vehicles?
Differential gears play a significant role in enhancing the handling and stability of vehicles. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Differential gears contribute to handling and stability in vehicles in several ways:
1. Independent Wheel Rotation:
One of the primary contributions of differential gears is allowing the wheels to rotate independently. During turns, the outer wheel needs to travel a greater distance than the inner wheel. The differential gear enables this speed differentiation, ensuring that each wheel can rotate at a different speed while still receiving power from the engine. This independent wheel rotation enables smoother and more controlled handling during turns.
2. Balanced Power Distribution:
The differential gear distributes torque between the wheels, allowing them to receive power and propel the vehicle forward. By balancing the power distribution, the differential helps maintain stability during acceleration and deceleration. It ensures that both wheels receive an appropriate amount of power, preventing excessive wheel spin or traction loss, which can affect the vehicle’s stability.
3. Enhanced Traction:
Effective traction is crucial for handling and stability. Differential gears play a key role in optimizing traction. In situations where one wheel encounters reduced traction, such as on slippery surfaces or during cornering, the differential allows the wheel with better traction to receive more power. This torque distribution helps maximize the vehicle’s ability to maintain forward motion and improves overall stability by minimizing wheel slip.
4. Improved Steering Response:
The differential gear contributes to improved steering response, which is essential for handling and stability. By allowing the wheels to rotate independently, the differential enhances the vehicle’s ability to respond to steering inputs. It enables precise and controlled turning, allowing the driver to navigate corners and curves with better accuracy and confidence.
5. Balanced Weight Distribution:
Proper weight distribution is critical for optimal handling and stability. The differential gear helps maintain balanced weight distribution among the wheels. During turns, the weight of the vehicle shifts towards the outside wheels. The differential allows the outer wheel to rotate faster, accommodating this weight transfer and promoting stability. By ensuring balanced weight distribution, the differential contributes to predictable and controlled handling.
6. Prevention of Wheel Hop:
Wheel hop, which refers to the rapid up-and-down movement of the wheels during acceleration or on uneven surfaces, can negatively impact stability and handling. The differential gear helps prevent wheel hop by allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds. This flexibility in wheel rotation reduces the likelihood of wheel hop, improving stability and maintaining better traction on the road.
In summary, differential gears contribute significantly to handling and stability in vehicles. They enable independent wheel rotation, balance power distribution, optimize traction, improve steering response, maintain balanced weight distribution, and prevent wheel hop. By facilitating smooth and controlled handling, the differential gear enhances the overall stability and performance of vehicles.


editor by Dream 2024-05-14
China Good quality Cut Cast Steel OEM Helical Cement Mixer Hunting Cylindrical Gear Hot Sale bevel gear set
Product Description
My advantages:
1. High quality materials, professional production, high-precision equipment. Customized design and processing;
2. Strong and durable, strong strength, large torque and good comprehensive mechanical properties;
3. High rotation efficiency, stable and smooth transmission, long service life, noise reduction and shock absorption;
4. Focus on gear processing for 20 years.
5. Carburizing and quenching of tooth surface, strong wear resistance, reliable operation and high bearing capacity;
6. The tooth surface can be ground, and the precision is higher after grinding.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
|---|---|
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Cut Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Bevel Wheel |
| Material: | Cast Steel |
| Type: | Worm And Wormwheel |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do you prevent backlash and gear play in a helical gear mechanism?
In a helical gear mechanism, preventing backlash and gear play is crucial to ensure accurate motion control, minimize vibration, and maintain the overall efficiency of the system. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to prevent backlash and gear play in a helical gear mechanism:
- Proper Gear Pair Alignment: Ensuring proper alignment of the gear pairs is essential to minimize backlash and gear play. Precise alignment helps to achieve optimal contact between the helical gear teeth, reducing gaps and potential for play. Proper alignment can be achieved through accurate positioning of the gear shafts and the use of alignment tools, such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems.
- Preload or Axial Play Adjustment: Applying a preload to the helical gears can help eliminate backlash and gear play. Preload refers to the intentional application of a force that compresses the gear mesh, ensuring a tight fit between the gear teeth. This can be achieved by using adjustable bearings, shims, or axial play adjustment mechanisms to control the axial position of the gears. By applying an appropriate preload, the gear teeth are kept in constant contact, minimizing any play or backlash.
- Accurate Gear Tooth Profile: High-quality manufacturing and accurate tooth profile design are essential to minimize backlash and gear play. The tooth profile should be precisely calculated to ensure proper engagement and minimal clearance between the gear teeth. This includes considerations such as the helix angle, tooth thickness, and tooth contact pattern. By using well-designed gear teeth with tight tolerances, backlash and gear play can be significantly reduced.
- Proper Gear Mesh Lubrication: Adequate lubrication is critical to reduce friction, wear, and the potential for backlash in helical gears. The lubricant helps to create a thin film between the mating gear surfaces, ensuring smooth and consistent gear meshing. Proper lubrication also helps to dissipate heat generated during operation, preventing gear tooth damage. The selection of a suitable lubricant and regular maintenance of the lubrication system are essential to prevent backlash and ensure optimal gear performance.
- Stiff Gearbox Design: A stiff and rigid gearbox design can help minimize gear play and backlash. The gearbox housing and supporting structures should be designed to withstand the forces and loads generated during operation. This prevents any flexing or movement of the gear components, ensuring stable gear meshing and minimizing the potential for backlash. Stiffening measures can include using robust materials, adequate bracing, and reinforcing the gearbox housing.
- Regular Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of the helical gear mechanism are essential to prevent backlash and gear play. This includes checking for any signs of wear, misalignment, or damage in the gear teeth, bearings, and housing. Any worn or damaged components should be promptly replaced to maintain the integrity of the gear system. Regular lubrication and cleanliness of the gears also contribute to minimizing backlash and ensuring smooth operation.
By implementing these preventive measures, engineers can effectively minimize backlash and gear play in a helical gear mechanism. This results in improved precision, reduced vibration, and enhanced overall efficiency of the gear system.

Can helical gears be used in precision manufacturing equipment?
Yes, helical gears can be used in precision manufacturing equipment, and they are often chosen for their specific advantages in such applications. Helical gears offer several features that make them suitable for precision manufacturing equipment. Here is a detailed explanation:
- Smooth and Precise Operation: Helical gears provide smooth and precise operation due to their gradual engagement of teeth. The helical tooth profile allows for gradual contact between mating gears, resulting in reduced noise, vibration, and backlash. The smooth operation is essential in precision manufacturing equipment where precise motion control and accuracy are required.
- High Load Capacity: Helical gears have high load-carrying capacity due to the larger contact area between the teeth compared to other gear types. This feature is beneficial in precision manufacturing equipment that may encounter heavy loads or high torque requirements. The increased load capacity ensures the gears can withstand the forces involved in precision machining or manufacturing processes.
- Efficiency: Helical gears can achieve high efficiency levels, especially when properly designed and manufactured. The helical tooth profile allows for efficient power transmission with minimal energy losses. In precision manufacturing equipment, high efficiency is desirable to maximize the utilization of input power and minimize heat generation.
- Compact Design: Helical gears have a compact design that allows for efficient use of space in precision manufacturing equipment. The helical gear configuration can provide a higher gear ratio in a smaller package compared to other gear types, making it suitable for equipment with limited space or complex layouts.
- Wide Range of Applications: Helical gears are versatile and can be used in various precision manufacturing equipment. They are commonly found in gearboxes, machine tools, milling machines, lathes, robotics, printing presses, and other equipment where precise motion control and high accuracy are required.
When using helical gears in precision manufacturing equipment, it is crucial to consider factors such as gear quality, material selection, lubrication, and proper alignment. High-quality gear manufacturing processes, accurate gear tooth profiles, and precise gear alignment are essential for achieving the desired precision and performance in manufacturing equipment.
Overall, helical gears are a popular choice in precision manufacturing equipment due to their smooth operation, high load capacity, efficiency, and compact design. Their versatility and ability to deliver precise motion control make them well-suited for various applications in precision manufacturing.
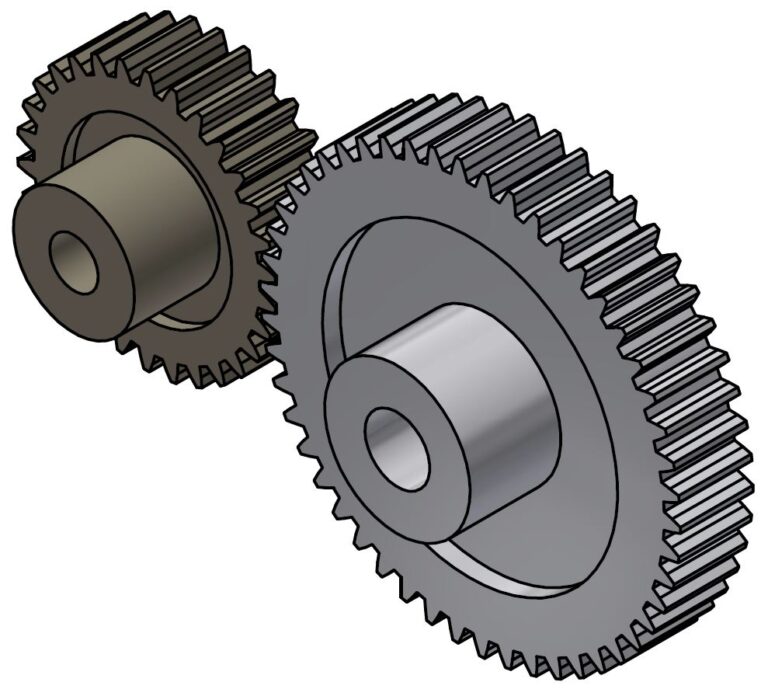
How do helical gears differ from other types of gears?
Helical gears possess distinct characteristics that set them apart from other types of gears. Here’s a detailed explanation of how helical gears differ from other gear types:
1. Tooth Orientation: Unlike spur gears, which have teeth perpendicular to the gear axis, helical gears have teeth that are cut at an angle to the gear axis. This helical tooth orientation enables gradual engagement and disengagement of the gear teeth, resulting in smoother and quieter operation.
2. Contact Pattern: Helical gears have a larger contact area compared to spur gears. The helical tooth design allows for multiple teeth to be in contact simultaneously, distributing the load across a broader surface. This increased contact pattern enhances load-carrying capacity and improves the gear’s ability to transmit higher torque.
3. Tooth Engagement: In helical gears, the teeth gradually mesh as they come into contact during rotation. This gradual engagement reduces the impact and noise typically associated with spur gears. The sliding action between the helical teeth also generates axial forces, resulting in a thrust load along the gear axis.
4. Load Distribution: The helical tooth orientation enables load distribution along the tooth face. This characteristic helps minimize localized stress concentrations and tooth wear, resulting in improved gear durability and longevity.
5. Power Transmission Efficiency: Helical gears offer high power transmission efficiency due to their larger contact area and gradual tooth engagement. The sliding action between the teeth introduces some axial force and axial thrust, which must be properly supported, but overall, helical gears are efficient in transmitting power.
6. Parallel Shaft Alignment: Helical gears are primarily used for parallel shaft applications. They transmit motion and power between parallel shafts with a constant speed ratio. Other gear types, such as bevel gears or worm gears, are better suited for non-parallel shaft arrangements or specific motion requirements.
7. Noise and Vibration: Compared to spur gears, helical gears produce less noise and vibration due to their gradual tooth engagement. The helical tooth design reduces the impact and noise caused by abrupt contact between gear teeth, resulting in smoother and quieter operation.
8. Manufacturing Complexity: Helical gears are more complex to manufacture compared to spur gears due to the helical tooth profile. The angled teeth require specialized cutting tools and machining processes. This complexity can affect the manufacturing cost and lead time of helical gears.
9. Axial Thrust Load: Helical gears generate axial forces and thrust loads due to the sliding action between the teeth. This axial thrust must be considered and properly supported in the gear system design to ensure smooth operation and prevent excessive wear or failure.
10. Application Range: Helical gears are versatile and find applications across various industries. They are commonly used in power transmission, robotics, machine tools, automotive systems, and other mechanical systems that require precise motion control and high torque transmission.
In summary, helical gears differ from other gear types in terms of tooth orientation, contact pattern, tooth engagement, load distribution, power transmission efficiency, shaft alignment suitability, noise and vibration characteristics, manufacturing complexity, axial thrust load, and application range. These unique characteristics make helical gears well-suited for specific applications where smooth operation, high load-carrying capacity, and precise motion control are required.


editor by Dream 2024-05-13
China Standard Front Axle Spider Differential Gear Txz356 for I Suzu gear patrol
Product Description
Product Description
| Gear model | Customized gear accoding to customers sample or drawing |
| product name | Customized Bevel Gear for Reducer/ Oil Drilling Rig/ Construction Machinery/ Truck |
| material | stainless steel , iron , aluminum ,bronze ,carbon steel ,brass , nylon etc . |
| size | ISO standard ,customer requirements |
| BORE | Finished bore, Pilot Bore, Special request |
| surface treatment | Carburizing and Quenching,Tempering ,Tooth suface high quenching Hardening,Tempering |
| Processing Method | Molding, Shaving, Hobbing, Drilling, Tapping, Reaming, Manual Chamfering, Grinding etc |
| Heat Treatment | Quenching & Tempering, Carburizing & Quenching, High-frequency Hardening, Carbonitriding…… |
| Package | Wooden Case/Container and pallet, or made-to-order |
| Certificate | ISO9001 TS16949 |
| Machining Process | Gear Hobbing, Gear Milling, Gear Shaping, Gear Broaching, Gear Shaving, Gear Grinding and Gear Lapping ,gear accuracy testing |
Detailed Photos
Certifications
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
ZheJiang Province Tonging Auto Synchronizer Co., Ltd and ZheJiang
Shshi Xihu (West Lake) Dis.g Gears Co. Ltd are focus on the production of space parts for the CHINAMFG over 35years. a professional company in the field.
Our spare parts are interchangeable with the major manufacturers of heavy duty trucks, buses, light commercial and 4×4 pick up vehicles, medium and heavy duty Japanese applications. New items developing for customized in earthmover and agriculture machines.
There are 1 forging production line of 1600 tons, several forging
production lines from 400 tons to 1000 tons: more than 300 various
manufacturing and inspecting equipments with high efficiency and
precision; 2 heat treatment production lines.
FAQ
| Q1. What is your terms of packing? |
| A: Generally, we pack our goods in Crates/Pallet/Boxes/Cartons. |
| Q2. How about your delivery time? |
| A: Generally, it is 3-7days if the goods are in stock,or it is need 20-30days to producing, |
| it is according to the quantity. |
| Q3. Can you produce according to the samples? |
| A: Yes, we can produce by your samples or technical drawings. We can build the molds and fixtures. |
| Q4. Do you test all your goods before delivery? |
| A: Yes, we have 100% test before delivery |
| Q5.Do you provide samples?is it free or extra? |
| A:yes,we could offer the sample for free,but do not pay the cost of freight. |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 100% Full Inspection |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Type: | Steering Bearing |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
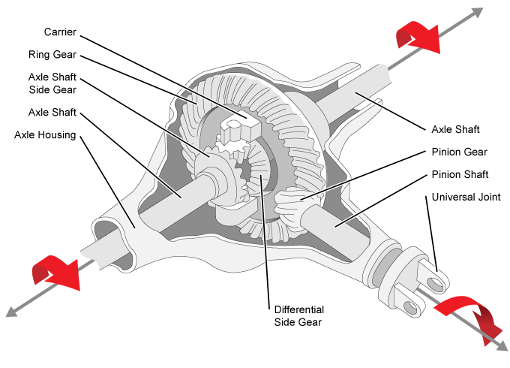
How do you address noise and vibration issues in a differential gear system?
Noise and vibration issues in a differential gear system can be concerning and may indicate underlying problems. Here are several steps that can be taken to address these issues:
- 1. Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the differential gear system for any visible signs of damage, leaks, or loose components. Check the differential housing, seals, and related components for any abnormalities. This can help identify any obvious issues that may be causing the noise or vibration.
- 2. Fluid Check: Ensure that the differential gear system has the proper amount of fluid and that the fluid is in good condition. Low or contaminated fluid can contribute to noise and vibration problems. If necessary, drain and replace the differential fluid following the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- 3. Lubrication: Proper lubrication is essential for smooth operation of the differential gears. If the noise or vibration issues persist, consider applying a high-quality gear lubricant recommended by the vehicle manufacturer. Ensure that the lubricant meets the required specifications.
- 4. Tightening and Adjustment: Check for any loose fasteners or components in the differential gear system. Tighten any bolts or nuts that may have come loose. Additionally, verify that the differential gears are properly adjusted and aligned. Incorrect gear meshing or misalignment can cause noise and vibration problems.
- 5. Bearing Inspection and Replacement: Worn or damaged bearings can contribute to noise and vibration. Inspect the differential bearings for signs of wear, pitting, or excessive play. If any issues are detected, replace the faulty bearings with new ones of the appropriate size and specification.
- 6. Gear Replacement: If the differential gears themselves are worn, chipped, or damaged, they may need to be replaced. Gears with significant wear or damage can cause noise and vibration. Consult a professional mechanic or technician for an accurate assessment and to determine if gear replacement is necessary.
- 7. Seals Replacement: Damaged or worn seals can allow contaminants to enter the differential gear system, leading to noise and vibration. Replace any faulty seals to ensure a proper seal and prevent fluid leaks.
- 8. Professional Diagnosis: If the noise and vibration issues persist despite these measures, it is advisable to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or technician. They have the expertise and specialized tools to diagnose complex differential gear problems accurately. They may perform additional tests, such as a gear backlash measurement or a comprehensive inspection of the gears and bearings, to identify the source of the issues.
It’s important to address noise and vibration issues in a differential gear system promptly to prevent further damage and ensure safe and smooth vehicle operation. Regular maintenance, including fluid checks and gear inspections, can help detect potential problems early and prevent more significant issues from arising.

What are the considerations for choosing the right type of differential gear for a vehicle?
When selecting the appropriate type of differential gear for a vehicle, several considerations come into play. Choosing the right differential gear involves assessing factors such as vehicle characteristics, intended use, driving conditions, and desired performance. Here’s a detailed explanation of the considerations for choosing the right type of differential gear:
- Vehicle Type: The type of vehicle, whether it’s a passenger car, SUV, truck, or performance vehicle, plays a significant role in determining the appropriate differential gear. Different types of vehicles have varying weight distributions, power outputs, and handling characteristics, which influence the optimal choice of differential gear.
- Driving Conditions: The intended driving conditions are crucial in selecting the right differential gear. Factors such as road surface, weather conditions, and terrain should be considered. For example, vehicles driven primarily on paved roads may benefit from different differential gear options compared to off-road vehicles that frequently encounter challenging terrain or vehicles that operate in regions with snowy or icy conditions.
- Performance Requirements: The desired performance attributes of the vehicle are important considerations. Some drivers prioritize acceleration and high-speed performance, while others focus on off-road capabilities, towing capacity, or fuel efficiency. Differential gears can be chosen to optimize specific performance aspects, such as maximizing traction, improving handling, enhancing torque delivery, or achieving better fuel economy.
- Traction Needs: The level of traction required is a key factor in selecting the right differential gear. Vehicles that need maximum traction in challenging conditions, such as racing cars, off-road vehicles, or vehicles used in low-grip environments, may benefit from limited-slip differentials or locking differentials. These differential types help distribute power to the wheels with the most grip, enhancing traction and maintaining vehicle control.
- Driving Dynamics: The desired driving dynamics and handling characteristics also influence the choice of differential gear. Some drivers prefer a more predictable and balanced handling, while others may desire more aggressive cornering capabilities. Differential gears with specific characteristics, such as torque vectoring differentials, can enhance these driving dynamics by actively managing torque distribution between individual wheels.
- Budget: Cost considerations are also significant when choosing a differential gear. Different types of differential gears vary in terms of complexity, features, and pricing. It’s essential to evaluate the budget constraints and weigh the cost against the desired performance benefits and requirements.
In summary, selecting the right type of differential gear for a vehicle involves considering factors such as vehicle type, driving conditions, performance requirements, traction needs, driving dynamics, and budget. By carefully assessing these considerations, drivers can choose a differential gear that aligns with their vehicle’s characteristics, intended use, and performance objectives, ultimately enhancing traction, handling, and overall driving experience.

What is the purpose of using a differential gear in an automobile?
A differential gear serves a crucial purpose in an automobile. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The purpose of using a differential gear in an automobile is to allow the wheels to rotate at different speeds while receiving power from the engine. It enables smooth and controlled maneuvering, optimizes traction, and enhances overall performance. The differential gear plays several key roles in an automobile:
1. Torque Distribution:
One of the primary purposes of a differential gear is to distribute torque (rotational force) from the engine to the wheels. As the engine generates power, the differential ensures that it is transmitted to the wheels efficiently and effectively. By dividing the torque between the two wheels, the differential enables both wheels to receive power and propel the automobile forward.
2. Differential Action:
The differential gear allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds when the automobile is turning or when one wheel encounters different traction conditions. This differential action is crucial for smooth and controlled maneuvering. By enabling the outer wheel to rotate faster than the inner wheel during a turn, the differential allows the automobile to negotiate corners without binding or skidding.
3. Wheel Speed Compensation:
When the automobile is turning, the inside wheel travels a shorter distance compared to the outside wheel. Without a differential gear, this speed difference would cause significant drivetrain stress and tire wear. The differential gear compensates for the varying wheel speeds by allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing strain on the drivetrain components.
4. Traction Improvement:
In situations where one wheel loses traction, such as when driving on slippery surfaces or uneven terrain, the differential gear helps improve traction. By allowing the wheel with traction to receive more power, the differential ensures that the automobile can continue moving forward. This is particularly important in automobiles with two-wheel drive, as the differential helps optimize power delivery to the wheel with better traction.
5. Reducing Tire Wear:
The differential gear contributes to reducing tire wear by accommodating differences in wheel speeds. By allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns, the differential minimizes tire scrubbing and uneven wear. It helps distribute the forces evenly across the tires, promoting longer tire life and maintaining better overall traction.
6. Enhanced Stability and Handling:
The differential gear plays a crucial role in enhancing automobile stability and handling. By allowing the wheels to rotate independently, the differential facilitates better control during turns and maneuvering. It helps maintain proper weight distribution, prevents excessive understeer or oversteer, and promotes balanced handling characteristics.
Overall, the purpose of using a differential gear in an automobile is to enable torque distribution, facilitate smooth and controlled maneuvering, optimize traction, reduce tire wear, and enhance stability and handling. The differential gear ensures that power is efficiently delivered to the wheels while accommodating varying speed and traction conditions, resulting in improved performance and driving dynamics.


editor by Dream 2024-05-13
China high quality Large Diameter Ring Gear Customized Girth Gear and Pinion Gear worm gearbox
Product Description
Key attributes
Other attributes
Applicable Industries
Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Repair Shops, Construction works
Weight (KG)
2000
Showroom Location
None
Video outgoing-inspection
Not Available
Machinery Test Report
Provided
Marketing Type
Ordinary Product
Warranty of core components
1 Year
Core Components
Gear
Place of CHINAMFG
ZheJiang , China
Condition
New
Warranty
1.5 years
Shape
Ring Gear
Standard or Nonstandard
Nonstandard
Tooth Profile
spur gear/helical gear/customized
Material
Steel
Processing
casting,Forging,hobbing
Pressure Angle
20/40/50/60 Customized
Brand Name
TS
Material
steel, stainless steel customized
Precision
standard precision grade per request
Technique
casting/forging/ customized
Heat Treatment
avaliable
Tooth Profile
Internal Spur/external spur/etc
Features
Professional Production
Application
Industry Machinery
Applicable Standard
ISO/DIN
Gear precision
ordinary/ 8e/7e/6e
Service
Customized OEM
Packaging and delivery
Packaging Details
TS Packaging Details:
1. Bearing surface is covered with the anti-rust oil first; And then wrapped with the plastic film;
2. And then packed with Kraft paper and professional belts;
3. At last, with wooden box totally at the outer packing to in void the rust or the moist;
4. Packaging can be done according to customer’s requirements.
Port
China any Port
Supply Ability
Supply Ability
1500 Set/Sets per Month
Show less
Lead time
| Quantity (sets) | 1 – 1 | > 1 |
| Lead time (days) | 30 | To be negotiated |
OUR WORKSHOPS
OUR EQUIPMENTS
Technology Process
|
Material |
Carbon steel,Alloy steel |
||
|
Structure |
Forging,casting |
||
|
Type of gear |
spur gear,helical gear,Planetary Gear |
||
|
Heat treatment |
Quenching and tempering |
||
|
Process |
forging, rough machining, QT, finish machining |
||
|
Main equipments |
hobbing,CNC machine |
||
|
Module |
up to 200 |
||
|
Precision of gear |
Grinding ISO Grade 5-7 & Hobbing ISO Grade 8-9 |
||
|
Inspection |
Raw material inspection, UT,physical property test,dimension inspect |
||
|
Application |
Mining machinery, mill, kiln and other equipment |
||
OUR CERTIFICATE
OUR CUSTOMER FEEDBACK
CONTACT
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industry |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hb190-Hb300 |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do you choose the right size ring gear for your application?
Choosing the right size ring gear for a specific application involves considering several factors related to the gear system, load requirements, space constraints, and performance objectives. Here’s a detailed explanation of the process involved in selecting the appropriate size ring gear:
- Determine the Gear System Parameters: Understand the specific requirements of the gear system in which the ring gear will be used. This includes identifying the input power, desired output speed, torque requirements, and operating conditions such as temperature, vibration, and lubrication.
- Calculate Gear Ratios: Determine the required gear ratios for the gear system. Gear ratios define the relationship between the rotational speeds and torques of the driving and driven gears. By knowing the desired gear ratios, you can calculate the appropriate size of the ring gear relative to the other gears in the system.
- Evaluate Load Capacity: Assess the load capacity needed for the application. Consider the maximum torque and radial loads that the ring gear will experience during operation. It’s crucial to select a ring gear that can handle the anticipated loads without excessive wear, deformation, or failure.
- Consider Space Limitations: Determine the available space for the ring gear within the application. Consider the overall dimensions, such as the outer diameter, inner diameter, and thickness of the ring gear. Ensure that the selected size fits within the designated space without interfering with other components or compromising the overall functionality of the system.
- Account for Manufacturing Considerations: Consider the manufacturability of the ring gear. Evaluate factors such as the feasibility of producing the required tooth profile, the availability of suitable materials, and the manufacturing capabilities of the supplier. It’s important to choose a size that can be efficiently manufactured while meeting the required quality standards.
- Consult Design Guidelines and Standards: Refer to industry design guidelines, standards, and specifications specific to the type of gear and application. These guidelines provide recommendations and formulas for calculating gear sizes based on factors such as tooth strength, contact stress, and bending stress. Adhering to recognized standards ensures that the selected ring gear size is appropriate for the intended application.
It is often beneficial to consult with gear design engineers or industry experts to ensure the proper selection of the ring gear size. They can provide detailed analysis, simulation, and expertise in choosing the optimal size based on the specific requirements and constraints of the application.
By carefully considering these factors and following established design practices, you can choose the right size ring gear that will deliver reliable performance, efficient power transmission, and long-term durability for your application.
\
What is the lifespan of a typical ring gear?
The lifespan of a typical ring gear can vary depending on various factors. Here’s a detailed explanation of the factors that influence the lifespan of a ring gear:
The lifespan of a ring gear is influenced by several factors, including:
- Material Quality: The quality of the material used to manufacture the ring gear plays a significant role in its lifespan. High-quality materials with good mechanical properties, such as hardened steel or alloys with high wear resistance, tend to have longer lifespans compared to lower-quality materials.
- Design and Load Conditions: The design of the ring gear, including its tooth profile, dimensions, and load-bearing capacity, affects its lifespan. Ring gears designed to handle higher loads and stresses are likely to have longer lifespans. The operating conditions, such as the magnitude and frequency of the torque loads, also impact the lifespan of the ring gear.
- Maintenance and Lubrication: Proper maintenance and lubrication are essential for preserving the lifespan of a ring gear. Regular inspection, cleaning, and lubrication of the gear system help reduce wear and prevent damage. Inadequate maintenance or the use of improper lubricants can accelerate wear and shorten the lifespan of the ring gear.
- Operating Environment: The operating environment in which the ring gear operates affects its lifespan. Factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, contaminants, and exposure to corrosive substances can impact the material integrity and performance of the ring gear. Harsh operating environments may lead to accelerated wear and reduced lifespan.
- Application-Specific Factors: The specific application in which the ring gear is used can influence its lifespan. Some applications may subject the ring gear to severe operating conditions, high-speed rotations, frequent starts and stops, or heavy shock loads, which can affect its durability and longevity. The accuracy of gear alignment, proper installation, and any additional factors specific to the application should be considered to assess the ring gear’s lifespan.
Given these factors, it is challenging to provide a specific lifespan for a typical ring gear. Lifespan estimates can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands or even millions of operating cycles or hours of operation. The longevity of a ring gear can be extended through proper selection of materials, careful design, routine maintenance, and adherence to recommended operating and lubrication practices.
It’s important to note that the lifespan of a ring gear can also depend on the presence of any unforeseen or exceptional circumstances, such as manufacturing defects, abnormal operating conditions, or unforeseen incidents that can cause premature failure. Regular inspection and monitoring of the gear system can help identify any signs of wear, damage, or potential issues, allowing for timely maintenance or replacement to ensure continued reliable operation.

What industries commonly use ring gears?
Ring gears, also known as annular gears or internal gears, are utilized in various industries due to their unique characteristics and capabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of the industries that commonly use ring gears:
- Automotive Industry: Ring gears are extensively used in the automotive industry. They are a crucial component in automotive transmissions, differential systems, and steering mechanisms. Ring gears help transmit torque and rotational motion, enabling smooth shifting of gears and efficient power transfer in vehicles.
- Aerospace Industry: The aerospace industry relies on ring gears for various applications. They are used in aircraft engines, landing gear systems, actuation mechanisms, and aerospace gearboxes. Ring gears provide reliable and precise motion control in critical aerospace systems.
- Industrial Machinery: Ring gears find wide applications in industrial machinery, including heavy machinery, manufacturing equipment, and power generation systems. They are used in gearboxes, speed reducers, and other power transmission systems. Ring gears enable efficient torque transfer and motion control in industrial settings.
- Robotics: Ring gears play a significant role in robotics and automation. They are employed in robotic joints, manipulator arms, and motion control systems. Ring gears provide precise and smooth rotation, allowing robots to perform intricate tasks with accuracy and repeatability.
- Power Generation: Ring gears are utilized in power generation equipment such as wind turbines, hydroelectric generators, and steam turbines. They are part of the gearbox systems that convert the rotational motion of the turbine blades into electrical energy. Ring gears enable efficient power transmission and adaptability to varying load conditions.
- Heavy Equipment and Construction: The heavy equipment and construction industry extensively use ring gears in equipment like excavators, cranes, loaders, and bulldozers. They are vital for the operation of the drivetrain and hydraulic systems, enabling controlled movement and power transfer in demanding construction environments.
- Marine Industry: Ring gears are employed in various marine applications, including ship propulsion systems, marine winches, and steering mechanisms. They provide reliable torque transfer and motion control in marine vessels, ensuring efficient navigation and maneuverability.
- Renewable Energy: Ring gears are utilized in renewable energy systems such as solar tracking systems and tidal power generation. They enable the precise tracking of solar panels and the efficient conversion of tidal forces into electrical energy.
The diverse applications of ring gears across these industries highlight their versatility and importance in various mechanical systems. The specific design, size, and material selection of ring gears may vary depending on the industry requirements and operating conditions.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China Custom Custom Industrial Equipment Cast Steel Cutting Planetary Gear / Bevel Gear bevel gear set
Product Description
1) According to the different strength and performance, we choose the steel with strong compression;
2) Using Germany professional software and our professional engineers to design products with more reasonable size and better performance; 3) We can customize our products according to the needs of our customers,Therefore, the optimal performance of the gear can be exerted under different working conditions;
4) Quality assurance in every step to ensure product quality is controllable.
Product Paramenters
| DRIVEN GEAR |
NUMBER OF TEETH |
10 |
|
MODULE |
12.35 | |
|
LENTH |
326 |
|
|
OUTER DIAMETER |
ø171.6 |
|
|
DIRECTION OF SPIRAL |
R |
|
|
ACCURACY OF SPLINE |
M50*2-6g |
|
|
NUMBER OF SPLINE |
50 |
|
DRIVEN GEAR |
NUMBER OF TEETH |
37 |
|
OUTER DIAMETER |
ø455 |
|
|
DIAMETER OF INNER HOLE |
ø250.84 |
|
|
ACCURACY OF SCREW |
12-ø16.5 |
|
|
CENTER DISTANCE OF SCREW HOLE |
ø282.575 |
|
|
DIRECTION OF SPIRAL |
L |
Company Profiles
Our company,HangZhou CHINAMFG Gear co.,Ltd , specialized in Hypoid and spiral bevel gear used in Automotive industry, was foundeded in 1996, with registered capital 136,8 square meter, with building area of 72,000 square meters. More than 500 employees work in our company.
We own more than 560 high-precise machining equipments, 10 Klingelnberg Oerlikon gear production lines, 36 Gleason gear production lines, 5 forging production lines 2 german Aichilin and 5 CHINAMFG CHINAMFG advanced automatic continuous heat treatment production lines. With the introducing the advanced Oerlikon C50 and P65 measuring center, we enhence our technology level and improve our product quality a lot. We offer better quality and good after-sale service with low price, which insure the good reputation. With the concept of “for the people, by technology, creativity, for the society, transfering friendship, honest”, we are trying to provice the world-top level product.
Our aim is: CHINAMFG Gear,world class, Drive the world.
According to the different strength and performance, we choose the steel with strong compression;Using Germany professional software and our professional engineers to design products with more reasonable size and better performance;We can customize our products according to the needs of our customers,Therefore, the optimal performance of the gear can be exerted under different working conditions;Quality assurance in every step to ensure product quality is controllable.
Our company had full quality management system and had been certified by ISO9001:2000, QS-9000:1998, ISO/TS16949 , which insure the entrance of international market.
Certification & honors
Packaging & Shipping
Packaging Detail:standard package(carton ,wooden pallet).
Shipping:Support Sea freight. Accept FOB,EXW,FAS,DES.
Cooperative customers
HangZhou CHINAMFG Gear Co., Ltd. adheres to the concept of “people-oriented, prosper with science and technology; create high-quality products, contribute to the society; turn friendship, and contribute sincerely”, and will strive to create world automotive axle spiral bevel gear products.
1.Do you provide samples?
Yes,we can offer free sample but not pay the cost of freight.
2.What about OEM?
Yes,we can do OEM according to your requirements.
3.How about after-sales service?
We have excellent after-sales service if you have any quanlity problem,you can contact us anytime.
4.What about package?
Stardard package or customized package as requirements.
5.How to ensure the quanlity of the products?
We can provide raw meterial report,metallographic examination and the accuracy testing etc.
6.How long is your delivery time?
Genarally it is 4-7 days.If customized it will be take 20 days according to your quantity. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Cast Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Herringbone Gear |
| Material: | Cast Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 131/Set
1 Set(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Are bevel gears suitable for high-torque applications?
Bevel gears can indeed be suitable for high-torque applications, depending on various factors such as the specific design, material selection, and proper application engineering. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Bevel gears are known for their ability to transmit power between intersecting shafts at different angles. They can handle significant torque loads and are commonly used in applications that require high-torque transmission. However, the suitability of bevel gears for high-torque applications depends on the following factors:
- Design: The design of the bevel gears plays a crucial role in their ability to handle high torque. Factors such as tooth profile, size, and geometry impact the load-carrying capacity and torque transmission capability. Bevel gears with robust and optimized designs, including suitable tooth profiles and adequate tooth engagement, can effectively handle high-torque applications.
- Material Selection: The choice of materials for bevel gears is critical in high-torque applications. Gears need to be made from materials with high strength, hardness, and wear resistance to withstand the forces and stresses involved in transmitting high torque. Common materials used for bevel gears include alloy steels, carburizing steels, and specialty alloys. Material selection should consider the specific torque requirements, operating conditions, and anticipated loads to ensure the gears can handle the desired torque levels.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication is essential for reducing friction, wear, and heat generation in high-torque bevel gear applications. Adequate lubrication helps maintain a lubricating film between the gear teeth, minimizing metal-to-metal contact and associated losses. The lubricant type, viscosity, and replenishment schedule should be selected based on the torque and operating conditions to ensure effective lubrication and minimize gear wear.
- Gear Size and Ratio: The size of the bevel gears and the gear ratio can influence their torque-handling capability. Larger gears generally have greater tooth strength and load-carrying capacity, making them more suitable for high-torque applications. The gear ratio should also be considered to ensure it is appropriate for the desired torque transmission and to avoid excessive loads on the gears.
- Operating Conditions: The operating conditions, including speed, temperature, and shock loads, must be taken into account when determining the suitability of bevel gears for high-torque applications. Higher speeds and extreme operating temperatures can affect the gear material properties, lubrication performance, and overall gear system efficiency. Proper cooling, temperature control, and gear protection measures should be implemented to maintain reliable performance under high-torque conditions.
By considering these factors and properly engineering the bevel gear system, it is possible to utilize bevel gears in high-torque applications effectively. However, it is crucial to consult with experienced engineers and perform thorough analysis and testing to ensure the gears can handle the specific torque requirements of the application.

Can bevel gears be used in automotive applications?
Yes, bevel gears can be used in automotive applications due to their unique characteristics and ability to transmit power between intersecting shafts at different angles. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Bevel gears are commonly found in various automotive systems and components, offering several advantages for specific applications. Here are some key automotive applications where bevel gears are utilized:
- Differential: One of the primary applications of bevel gears in automotive systems is in the differential mechanism. The differential is responsible for distributing torque between the drive wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds, especially during cornering. Bevel gears, specifically hypoid gears, are used in the differential to transfer power from the driveshaft to the wheel axles at right angles. The compact size and high torque transmission capability of bevel gears make them suitable for this critical drivetrain component.
- Power Transfer: Bevel gears are utilized in automotive power transfer systems, such as transfer cases and drivelines. Transfer cases, commonly found in four-wheel drive (4WD) and all-wheel drive (AWD) vehicles, transfer power from the transmission to the front and rear axles. Bevel gears enable the necessary change in direction and torque transmission between the input and output shafts of the transfer case. Similarly, bevel gears can be used in drivelines to transfer power between differentials or between the transmission and the axles.
- Steering Systems: Bevel gears play a role in automotive steering systems, particularly in rack-and-pinion steering mechanisms. In these systems, bevel gears are used to convert the rotational motion of the steering wheel into the linear motion required for steering. Bevel gears help change the direction of motion, enabling the driver to control the vehicle’s steering angle. The compact size and precise motion transmission characteristics of bevel gears make them suitable for these steering applications.
- Auxiliary Systems: Bevel gears find application in various auxiliary automotive systems. For example, they can be used in engine timing systems to drive camshafts and synchronize valve operation. Bevel gears can also be employed in automotive differentials with limited-slip or locking capabilities, enhancing traction and vehicle stability in challenging road conditions. Additionally, they can be found in power seat adjusters, sunroof mechanisms, and other vehicle systems where torque transmission at different angles is required.
Bevel gears used in automotive applications are typically designed to withstand high loads, operate with minimal noise and vibration, and provide reliable power transmission. They are often manufactured from durable materials, such as alloy steels, and undergo heat treatment processes to enhance their strength and wear resistance.
It is important to note that the specific design and selection of bevel gears for automotive applications depend on factors such as torque requirements, space limitations, operating conditions, and cost considerations. Gear engineers and automotive manufacturers carefully consider these factors to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability in automotive systems.
In summary, bevel gears are extensively used in automotive applications, including differentials, power transfer systems, steering mechanisms, and auxiliary systems. Their ability to transmit power at varying angles, compact size, and robust construction make them well-suited for the demanding requirements of the automotive industry.

What are the applications of a bevel gear?
A bevel gear finds applications in various industries and mechanical systems where changes in direction or speed of rotational motion are required. Here’s a detailed explanation of the applications of a bevel gear:
- Automotive Industry: Bevel gears are widely used in the automotive industry, particularly in differentials. Differentials are responsible for distributing torque between the driving wheels of a vehicle, allowing them to rotate at different speeds when turning. Bevel gears in differentials transmit power from the engine to the wheels, enabling smooth cornering and improved traction.
- Mechanical Power Transmission: Bevel gears are employed in mechanical power transmission systems to change the direction of rotational motion. They are used in applications such as power tools, machine tools, conveyors, and printing presses. By meshing with other bevel gears or with spur gears, they transmit torque and power efficiently from one shaft to another, accommodating changes in direction and speed.
- Marine Propulsion Systems: Bevel gears are extensively used in marine propulsion systems, including boats and ships. They are commonly found in the propulsion shaft line, where they transmit torque from the engine to the propeller shaft, allowing the vessel to move through water. Bevel gears in marine applications are designed to withstand high loads, resist corrosion, and operate efficiently in harsh environments.
- Aerospace Industry: Bevel gears are utilized in various aerospace applications. They are employed in aircraft landing gear systems, where they transmit torque from the hydraulic motor to extend or retract the landing gear. Bevel gears are also found in helicopter rotor systems, providing the necessary power transmission to rotate the rotor blades.
- Railway Systems: Bevel gears play a crucial role in railway systems, particularly in locomotives and rolling stock. They are used in the transmission systems to transfer power from the engine to the wheels. Bevel gears ensure smooth and efficient power transfer, enabling the train to move forward or backward while negotiating curves on the track.
- Industrial Machinery: Bevel gears are extensively employed in various industrial machinery, such as milling machines, lathes, and industrial robots. They facilitate changes in direction and speed of rotational motion, enabling precise positioning, accurate cutting, and smooth operation of the machinery.
- Mining and Construction Equipment: Bevel gears are used in mining and construction equipment to transfer power and torque in heavy-duty applications. They are found in equipment such as excavators, bulldozers, and crushers, where they provide reliable power transmission in challenging environments.
These are just a few examples of the applications of bevel gears. Their ability to transmit power, change the direction of rotational motion, and accommodate intersecting shafts makes them versatile and suitable for a wide range of industries and mechanical systems.
In summary, bevel gears are extensively utilized in automotive differentials, mechanical power transmission systems, marine propulsion systems, aerospace applications, railway systems, industrial machinery, and mining and construction equipment. Their applications span across industries where changes in direction or speed of rotational motion are essential for efficient and reliable operation.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China Professional Stainless Steel Spur Gears Motor Best Wheel Durable Diameter Bevel Shafts Pin Manufacturer Bore Tooth Brass Miniature Auto Cylindrical Stainless Steel Spur Gear with Hot selling
Product Description
Stainless Steel Spur Gears Motor Best Wheel Durable Diameter Bevel Shafts Pin Manufacturer Bore Tooth Brass Miniature Auto Cylindrical Stainless Steel Spur Gear
Spur gears are a type of cylindrical gear, with shafts that are parallel and coplanar, and teeth that are straight and oriented parallel to the shafts. They’re arguably the simplest and most common type of gear – easy to manufacture and suitable for an array of applications.
1.Material: Alloy Steel, Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Harden & Tempered Steel, Cast Iron, Aluminum, Copper, Brass nylon and so on.
2. Heat Treatment: Hardening and Tempering, High Frequency Quenching, Carburizing Quenching and so on.
3. Pilot bore, finished bore, taper bore and special bore.
4. Bright surface and high precision
5. Advanced heat treatment and surface treatment craft
6. Better quality and competitive price.
7. Convenient to transport and handle
8. High strength
9. Corrosion resistance
10. Easy to install
11. Long life span
12. OEM/ODM welcome
There are 2 primary types of spur gears: external and internal. Exterior gears have the teeth that are cut externally surface area of the cylinder. Two external gears mesh with each other and rotate in opposite directions. Internal gears, in contrast, have teeth that are cut on the inside surface of the cylinder. An external gear sits inside the internal gear, and the gears rotate in the same direction. Because the shafts are positioned closer together, internal gear assemblies are more compact than external gear assemblies. Internal gears are primarily used for planetary gear drives.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | Internal Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Rolling Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Cast Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

How do you calculate the efficiency of a spur gear?
Calculating the efficiency of a spur gear involves considering the power losses that occur during gear operation. Here’s a detailed explanation:
In a gear system, power is transmitted from the driving gear (input) to the driven gear (output). However, due to various factors such as friction, misalignment, and deformation, some power is lost as heat and other forms of energy. The efficiency of a spur gear represents the ratio of the output power to the input power, taking into account these power losses.
Formula for Calculating Gear Efficiency:
The efficiency (η) of a spur gear can be calculated using the following formula:
η = (Output Power / Input Power) × 100%
Where:
η is the efficiency of the gear system expressed as a percentage.
Output Power is the power delivered by the driven gear (output) in the gear system.
Input Power is the power supplied to the driving gear (input) in the gear system.
Factors Affecting Gear Efficiency:
The efficiency of a spur gear is influenced by several factors, including:
- Tooth Profile: The tooth profile of the gear affects the efficiency. Well-designed gear teeth with accurate involute profiles can minimize friction and power losses during meshing.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication between the gear teeth reduces friction, wear, and heat generation, improving gear efficiency. Insufficient or inadequate lubrication can result in increased power losses and reduced efficiency.
- Gear Material: The selection of gear material affects efficiency. Materials with low friction coefficients and good wear resistance can help minimize power losses. Higher-quality materials and specialized gear coatings can improve efficiency.
- Gear Alignment and Meshing: Proper alignment and precise meshing of the gear teeth are essential for optimal efficiency. Misalignment or incorrect gear meshing can lead to increased friction, noise, and power losses.
- Bearing Friction: The efficiency of a gear system is influenced by the friction in the bearings supporting the gear shafts. High-quality bearings with low friction characteristics can contribute to improved gear efficiency.
- Load Distribution: Uneven load distribution across the gear teeth can result in localized power losses and reduced efficiency. Proper design and gear system configuration should ensure even load distribution.
Interpreting Gear Efficiency:
The calculated gear efficiency indicates the percentage of input power that is effectively transmitted to the output. For example, if a gear system has an efficiency of 90%, it means that 90% of the input power is converted into useful output power, while the remaining 10% is lost as various forms of power dissipation.
It’s important to note that gear efficiency is not constant and can vary with operating conditions, lubrication quality, gear wear, and other factors. The calculated efficiency serves as an estimate and can be influenced by specific system characteristics and design choices.
By considering the factors affecting gear efficiency and implementing proper design, lubrication, and maintenance practices, gear efficiency can be optimized to enhance overall gear system performance and minimize power losses.

Are spur gears suitable for high-torque applications?
Spur gears are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including those involving high-torque requirements. However, their suitability for high-torque applications depends on various factors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Spur gears are designed to transmit power and torque between parallel shafts. They have straight teeth that engage fully, providing efficient power transfer. The suitability of spur gears for high-torque applications can be evaluated based on the following considerations:
- Load Distribution: Spur gears distribute the transmitted load over a larger contact area compared to other gear types. This characteristic allows them to handle higher torque loads effectively.
- Size and Diameter: The size and diameter of the spur gears play a crucial role in their ability to handle high torque. Larger gear diameters provide increased torque capacity due to the longer lever arm and larger contact area between the gear teeth.
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate material for the spur gears is essential for high-torque applications. Strong and durable materials, such as hardened steel or alloy steels, are commonly used to ensure the gears can withstand the high stresses and torque loads without deformation or failure.
- Gear Design: Proper gear design considerations, such as tooth profile, module or pitch, and the number of teeth, can impact the torque-carrying capacity of spur gears. Design parameters should be optimized to ensure sufficient tooth strength and minimize the risk of tooth breakage or excessive wear.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Adequate lubrication is critical for reducing friction, wear, and heat generation in high-torque spur gear applications. Regular maintenance, including lubricant replacement and gear inspections, can help identify and address any issues that may affect the gear’s torque-handling capabilities.
- Supporting Components: The overall system design, including the selection of bearings, shafts, and housing, should be considered to ensure proper support and alignment of the spur gears. Well-designed supporting components contribute to the overall torque capacity of the system.
While spur gears can handle high torque, it’s important to note that there are limitations to their torque capacity. Factors such as gear size, material strength, tooth design, and operating conditions can affect the maximum torque the gears can safely transmit without failure.
In some cases, other gear types such as helical gears or bevel gears may be more suitable for specific high-torque applications. These gears offer advantages such as increased load-carrying capacity, improved torque transfer efficiency, and reduced noise and vibration levels.
Ultimately, the suitability of spur gears for high-torque applications should be evaluated based on the specific requirements, operating conditions, and industry standards applicable to the particular application.

What industries commonly use spur gears?
Spur gears find wide applications across various industries due to their simplicity, efficiency, and versatility. Here’s a detailed explanation of the industries that commonly use spur gears:
- Automotive Industry: The automotive industry extensively utilizes spur gears in various components and systems. They are commonly found in gearboxes, differentials, transmission systems, and engine timing mechanisms. Spur gears play a crucial role in transferring power and rotational motion between the engine, wheels, and other drivetrain components.
- Machinery and Manufacturing: Spur gears are widely employed in machinery and manufacturing equipment across different sectors. They are used in conveyor systems, machine tools, printing presses, textile machinery, packaging machinery, and a variety of industrial applications. Spur gears facilitate power transmission and motion control in these systems.
- Power Generation: Spur gears are essential in power generation systems such as wind turbines, hydroelectric turbines, and steam turbines. They are used to transmit power from the rotor to the generator, converting the rotational motion of the turbine blades into electricity. Spur gears enable efficient power transfer in these renewable energy systems.
- Robotics and Automation: Spur gears have significant applications in robotics and automation systems. They are used in robotic joints, actuators, and drive systems to control motion and transmit torque accurately and efficiently. Spur gears enable precise movement and force transmission in robotic applications.
- Aerospace and Aviation: The aerospace and aviation industries utilize spur gears in various applications. They can be found in aircraft landing gear systems, engine components, flight control systems, auxiliary power units (APUs), and other critical equipment. Spur gears play a vital role in transmitting power and controlling movement in these aerospace systems.
- Marine and Shipbuilding: Spur gears are commonly used in the marine and shipbuilding industry. They find applications in propulsion systems, winches, steering mechanisms, and other equipment that require torque transmission and speed control. Spur gears enable efficient power transfer and maneuverability in marine vessels.
- Appliances and Household Equipment: Spur gears are present in numerous household appliances and equipment. They are used in washing machines, dishwashers, mixers, food processors, garage door openers, and many other appliances that require rotational motion and power transmission. Spur gears facilitate the efficient operation of these household devices.
- Power Tools: Spur gears are widely utilized in power tools such as drills, saws, grinders, and sanders. They enable the transmission of power from the motor to the tool’s cutting or grinding components, ensuring efficient and controlled operation. Spur gears contribute to the functionality and performance of power tools.
- Medical Equipment: Spur gears are used in various medical devices and equipment. They can be found in imaging systems, surgical robots, medical pumps, and other applications that require precise motion control and torque transmission. Spur gears play a critical role in the functioning of medical equipment.
- Clocks and Watches: Spur gears are a fundamental component in mechanical clocks and watches. They are responsible for accurate timekeeping by transferring rotational motion from the mainspring or oscillator to the hour, minute, and second hands. Spur gears have historical significance in timekeeping mechanisms.
These are just a few examples of the industries where spur gears are commonly used. Their simplicity, reliability, and efficiency make them a popular choice in a wide range of applications, enabling power transmission, motion control, and precise operation in diverse industrial sectors.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China high quality Cement Kiln Customized Casting Steel Large Diameter Ring Gear High Quality Rotary Girth Gear Spur Large Ring Gear bevel gear set
Product Description
Key attributes
Other attributes
Applicable Industries
Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Repair Shops, Energy & Mining
Weight (KG)
1650
Showroom Location
None
Video outgoing-inspection
Provided
Machinery Test Report
Provided
Marketing Type
Hot Product 2571
Warranty of core components
1 Year
Core Components
Gear
Place of CHINAMFG
ZheJiang , China
Condition
New
Warranty
1.5 years
Shape
Ring Gear
Standard or Nonstandard
Nonstandard
Tooth Profile
Spur
Material
Steel
Processing
Casting
Pressure Angle
20°
Brand Name
HangZhou
Product Name
custom large diameter alloy steel spur casting large ring gear
Application
Cement kiln
Gear Machining
Gear milling
Module of Gear:
8-120
OD For Gear Wheel:
MAX.13 000 mm
Height For CHINAMFG
MAX. 1200 mm
Certificate
ISO 9001:2015
Tolerance
+/-0.01mm
Heat treatment
QT
Surface Treatment
Surface Hardening or Carburizing and Quenching
Packaging and delivery
Packaging Details
Package for Cement kiln custom large diameter ring gear transmission alloy steel spur casting large ring gear is wooden box and adapts to CHINAMFG transport
Port
ZheJiang ,HangZhou or Others
Supply Ability
Supply Ability
9000 Ton/Tons per Year
OUR WORKSHOPS
OUR EQUIPMENTS
Technology Process
|
Material |
Carbon steel,Alloy steel |
||
|
Structure |
Forging,casting |
||
|
Type of gear |
spur gear,helical gear,Planetary Gear |
||
|
Heat treatment |
Quenching and tempering |
||
|
Process |
forging, rough machining, QT, finish machining |
||
|
Main equipments |
hobbing,CNC machine |
||
|
Module |
up to 200 |
||
|
Precision of gear |
Grinding ISO Grade 5-7 & Hobbing ISO Grade 8-9 |
||
|
Inspection |
Raw material inspection, UT,physical property test,dimension inspect |
||
|
Application |
Mining machinery, mill, kiln and other equipment |
||
OUR CERTIFICATE
OUR CUSTOMER FEEDBACK
CONTACT
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industry |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hb190-Hb300 |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Are there different types of ring gears available?
Yes, there are different types of ring gears available to suit various applications and functional requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of the different types of ring gears:
- External Ring Gears: External ring gears, also known as external annular gears, have teeth on the outer circumference of the gear. These gears mesh with an internal gear or a pinion gear. External ring gears are commonly used in applications where the gear rotation needs to be transferred to an internal gear or where a high gear ratio is desired.
- Internal Ring Gears: Internal ring gears, also known as internal annular gears, have teeth on the inner circumference of the gear. These gears mesh with an external gear or a pinion gear. Internal ring gears are frequently used in applications where the gear rotation needs to be transmitted to an external gear or where a compact gear assembly is required.
- Segmental Ring Gears: Segmental ring gears are ring gears that are divided into segments or sectors. Each segment has a portion of the gear’s circumference with teeth. These segments can be individually mounted or assembled together to form a complete ring gear. Segmental ring gears are used in applications where flexibility in gear installation or replacement is necessary, such as large-scale gear systems or machinery with limited access.
- Spur Ring Gears: Spur ring gears have straight teeth that are parallel to the gear’s axis of rotation. These gears offer simple and efficient operation with high gear ratios. Spur ring gears are commonly used in applications that require precise motion control, such as robotics, automotive transmissions, and industrial machinery.
- Helical Ring Gears: Helical ring gears have teeth with a helix angle. The helical teeth form a helical or spiral pattern around the gear’s circumference. Helical ring gears provide smoother and quieter operation compared to spur ring gears due to the gradual engagement of the teeth. They are often used in applications that demand high torque transmission, such as heavy machinery, marine propulsion systems, and power generation equipment.
- Bevel Ring Gears: Bevel ring gears have teeth that are conically shaped and intersect the gear’s axis of rotation. These gears are used in applications that require the transmission of motion and torque between shafts that are not parallel but intersect at an angle. Bevel ring gears are commonly found in automotive differentials, hand tools, and various industrial machinery.
- Planetary Ring Gears: Planetary ring gears are part of planetary gear systems, which consist of multiple gears arranged in a planetary configuration. The ring gear serves as the stationary outer gear, while other gears, such as sun gears and planet gears, revolve around it. Planetary ring gears are used in applications that require compact and efficient gear systems, such as automotive transmissions, robotics, and aerospace mechanisms.
The specific type of ring gear chosen for a particular application depends on factors such as load requirements, space limitations, gear ratios, operating conditions, and desired performance characteristics.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using ring gears?
Using ring gears in various applications offers several advantages and disadvantages. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages and disadvantages of using ring gears:
Advantages of Using Ring Gears:
- Efficient Power Transmission: Ring gears provide efficient power transmission by transmitting rotational energy and torque between components. They enable smooth and reliable transfer of power, resulting in efficient operation of the system.
- High Torque Capacity: Ring gears are designed to handle high torque loads. Their robust construction and large contact area between gear teeth allow for the transmission of substantial amounts of torque, making them suitable for applications that require high torque capacity.
- Compact Design: Ring gears have a compact design compared to other gear types, such as spur gears or helical gears. This compactness allows for space-saving installations, making ring gears suitable for applications with limited space or tight packaging requirements.
- Load Distribution: Ring gears distribute loads evenly across the gear system, preventing localized overloading and reducing the risk of premature component failure. They help ensure balanced operation and optimal load sharing among gears, resulting in improved system reliability.
- Versatility: Ring gears are versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications across various industries. They are found in automotive transmissions, industrial gearboxes, wind turbines, robotics, printing presses, and many other machinery and equipment types.
- Smooth and Quiet Operation: Well-designed ring gears with proper tooth profiles and tight tolerances can provide smooth and quiet operation. They minimize noise and vibrations, enhancing the overall user experience and reducing the need for additional noise reduction measures.
Disadvantages of Using Ring Gears:
- Complex Manufacturing: The manufacturing process for ring gears can be more complex compared to simpler gear types. The intricate geometry and tooth profiles of ring gears require precise machining and specialized manufacturing techniques, which may increase production costs.
- Higher Friction and Wear: Ring gears can generate higher levels of friction compared to other gear types. The sliding motion of the gear teeth during engagement can result in increased wear and heat generation. Proper lubrication and maintenance are necessary to minimize friction and ensure long-term durability.
- Backlash: Ring gears may exhibit a certain amount of backlash, which is the play or clearance between gear teeth when they change direction. Backlash can impact the accuracy and precision of the gear system, especially in applications that require high positioning or synchronization requirements. Minimizing backlash requires careful design and precise manufacturing.
- Complex Gear Meshing: Ring gears require proper gear meshing with other gears to ensure efficient power transmission. Achieving optimal gear meshing can be more challenging due to the curved profile of the ring gear. It requires careful design considerations and precise alignment to ensure smooth and reliable operation.
- Cost: Ring gears can be more expensive than simpler gear types due to their complex manufacturing process and specialized design requirements. The higher cost may be a consideration in applications with strict budget constraints or where alternative gear types can fulfill the required functionality.
It’s important to consider the specific requirements and constraints of the application when deciding whether to use ring gears. While they offer advantages such as efficient power transmission, high torque capacity, and compact design, they also have disadvantages related to manufacturing complexity, friction, backlash, and cost. Proper engineering analysis and evaluation can help determine the suitability of ring gears for a given application.

How do ring gears differ from other types of gears?
Ring gears, also known as annular gears or internal gears, possess distinct characteristics that set them apart from other types of gears. Here’s a detailed explanation of how ring gears differ from other gears:
1. Tooth Configuration: The most significant difference between ring gears and other gears is their tooth configuration. In a ring gear, the teeth are located on the inside circumference of a circular ring, whereas in other gears such as spur gears, helical gears, and bevel gears, the teeth are present on the outer surface of the gear. This internal tooth arrangement makes ring gears unique and allows them to mesh with pinion gears or other external gears.
2. Gear Assembly: The assembly of ring gears differs from other gears. In most cases, ring gears are used in combination with pinion gears or other external gears. The pinion gear meshes with the teeth on the inside of the ring gear. This gear set configuration enables the transmission of rotational motion and torque.
3. Load Distribution: Ring gears distribute the load over a larger area compared to other types of gears. The load is spread across the internal teeth of the ring gear, resulting in improved load-carrying capacity and enhanced gear durability. This load distribution characteristic makes ring gears suitable for applications that involve high loads or continuous operation.
4. Gear Ratio: Ring gears offer specific advantages in terms of gear ratios. They are commonly used in applications where high gear ratios are required. The gear ratio is determined by the number of teeth on the ring gear compared to the number of teeth on the mating gear (such as a pinion gear). The internal tooth configuration of the ring gear allows for larger gear diameters, enabling higher gear ratios to be achieved.
5. Space Utilization: Ring gears provide a compact design compared to some other types of gears. The internal tooth arrangement allows for a more space-efficient gear assembly. This compactness is advantageous in applications where space is limited or where a high gear ratio needs to be achieved within a confined area.
6. Applications: Ring gears are commonly used in automotive transmissions, differential systems, planetary gear systems, industrial machinery, robotics, power generation equipment, and heavy machinery. Their unique characteristics make them suitable for applications that require precise motion control, load distribution, and high gear ratios.
It’s important to note that the specific design, tooth profile, material selection, and manufacturing techniques may vary for different types of gears, including ring gears. Each type of gear is designed to meet specific application requirements, operating conditions, and performance needs.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China Best Sales Car Hardened Tooth Surface OEM Wooden Case Helical Rack Motorcycle Gear worm and wheel gear
Product Description
My advantages:
1. High quality materials, professional production, high-precision equipment. Customized design and processing;
2. Strong and durable, strong strength, large torque and good comprehensive mechanical properties;
3. High rotation efficiency, stable and smooth transmission, long service life, noise reduction and shock absorption;
4. Focus on gear processing for 20 years.
5. Carburizing and quenching of tooth surface, strong wear resistance, reliable operation and high bearing capacity;
6. The tooth surface can be ground, and the precision is higher after grinding.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Motorcycle, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Cut Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Cast Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
How do you maintain and service a helical gear system?
Maintaining and servicing a helical gear system is essential to ensure its long-term performance, reliability, and longevity. Proper maintenance practices help identify and address potential issues before they lead to gear failure or reduced efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to maintain and service a helical gear system:
- Regular Inspection: Perform regular visual inspections of the helical gear system to check for any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspect the gear teeth, shafts, bearings, and lubrication system for any abnormalities. Look for indications such as pitting, chipping, excessive tooth wear, or unusual noise or vibration during operation.
- Lubrication Maintenance: Ensure proper lubrication of the helical gears as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. Monitor lubricant levels, quality, and contamination. Periodically check and replenish or replace the lubricant as necessary. Follow the recommended lubrication intervals and use the appropriate lubricant type and viscosity for the operating conditions.
- Gear Cleaning: Keep the gear system clean and free from debris or contaminants. Regularly remove any accumulated dirt, dust, or foreign particles that may affect the gear performance. Use appropriate cleaning methods such as brushing, wiping, or compressed air to maintain a clean gear environment.
- Alignment Check: Misalignment can lead to premature gear failure and reduced efficiency. Periodically check the shaft alignment using precision alignment tools. Ensure that the shafts are properly aligned both radially and axially. If misalignment is detected, take corrective measures such as adjusting the shaft positions or using shims to reestablish proper alignment.
- Check Gear Meshing: Monitor the gear meshing to ensure proper tooth engagement and contact. Regularly inspect the tooth contact pattern to identify any irregularities or changes. If necessary, make adjustments to the gear position or shim thickness to achieve the desired tooth contact pattern and optimize gear performance.
- Bearing Maintenance: Check the condition of the bearings supporting the helical gears. Monitor for any signs of wear, damage, or inadequate lubrication. Replace worn-out or faulty bearings promptly to prevent further damage to the gear system. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for bearing maintenance, lubrication, and replacement.
- Vibration Analysis: Perform periodic vibration analysis to detect any abnormal vibration patterns that may indicate gear or bearing problems. Use vibration monitoring tools and techniques to identify the source and severity of the vibrations. If excessive vibrations are detected, investigate and rectify the underlying causes to prevent gear damage or failure.
- Temperature Monitoring: Monitor the temperature of the helical gear system during operation. Excessive heat can be an indication of inadequate lubrication, overloading, or other issues. Regularly measure and record the gear system’s operating temperature to identify any abnormal temperature rise and take appropriate action if necessary.
- Training and Documentation: Ensure that maintenance personnel are properly trained in helical gear system maintenance and servicing. Maintain detailed documentation of maintenance activities, including inspection records, lubrication schedules, and any repairs or replacements performed. This documentation helps track the gear system’s history and assists in troubleshooting and future maintenance planning.
- Consult with Experts: When in doubt or when dealing with complex gear systems, consult with gear manufacturers, industry experts, or experienced engineers for guidance on specific maintenance procedures or troubleshooting techniques. They can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on their expertise and experience.
By following these maintenance and servicing practices, you can ensure the optimal performance, reliability, and longevity of your helical gear system. Regular inspections, proper lubrication, alignment checks, and timely repairs or replacements are crucial for minimizing downtime, extending gear life, and maximizing the efficiency of the gear system.

How do you retrofit an existing mechanical system with helical gears?
Retrofitting an existing mechanical system with helical gears involves replacing the current gear system with helical gears to improve performance, efficiency, or address specific requirements. The process requires careful planning, analysis, and implementation to ensure a successful retrofit. Here is a detailed explanation of how to retrofit an existing mechanical system with helical gears:
- Assess the Existing System: Begin by thoroughly assessing the existing mechanical system. Understand its design, operating conditions, gear specifications, and performance limitations. Identify the reasons for retrofitting, such as the need for increased load capacity, improved efficiency, noise reduction, or other specific requirements.
- Define Retrofit Objectives: Clearly define the objectives of the retrofit. Determine the specific improvements or modifications desired from the retrofit. This could include increasing torque capacity, reducing backlash, improving gear meshing characteristics, or optimizing gear ratios. Having well-defined objectives will guide the retrofitting process.
- Perform Gear Design and Analysis: Based on the defined objectives, conduct gear design and analysis to determine the appropriate helical gear configuration. Consider factors such as gear size, tooth profile, helix angle, module or diametral pitch, and gear material. Use engineering calculations, software simulations, or consult with gear design experts to ensure the selected helical gears meet the retrofit objectives and are compatible with the existing system.
- Modify Gear Housing and Mounting: In some cases, retrofitting with helical gears may require modifications to the gear housing or mounting arrangements. Ensure that the gear housing can accommodate the helical gears and provide proper alignment and support. Modify or adapt the housing as necessary to ensure a precise fit and alignment of the new gear system.
- Manufacture or Source Helical Gears: Once the gear design is finalized, manufacture or source the helical gears according to the specifications determined during the design phase. Work with experienced gear manufacturers or suppliers who can provide high-quality helical gears that meet the required specifications and performance criteria.
- Installation and Alignment: Remove the existing gears and install the helical gears in the mechanical system. Ensure proper alignment of the gears to maintain smooth operation and minimize wear. Follow recommended installation procedures and torque specifications provided by the gear manufacturer. Consider using alignment tools, such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems, to achieve precise gear alignment.
- Test and Fine-tune: After installation, conduct thorough testing of the retrofit system. Monitor performance, check for any abnormal vibrations, noise, or operating issues. Fine-tune the system as needed, making adjustments to gear meshing, lubrication, or other parameters to optimize performance and ensure the retrofit objectives are met.
- Monitor and Maintain: Once the retrofit is complete, establish a regular monitoring and maintenance schedule. Periodically inspect the helical gears for wear, perform lubrication checks, and address any maintenance requirements. Regular monitoring and maintenance will help ensure the longevity and optimal performance of the retrofit system.
Retrofitting an existing mechanical system with helical gears can significantly enhance its performance, efficiency, and reliability. However, it is essential to carefully plan and execute the retrofitting process to achieve the desired outcomes. Consulting with gear design experts and experienced professionals can provide valuable guidance and expertise throughout the retrofitting process.

Are there different types of helical gears available?
Yes, there are different types of helical gears available to meet specific application requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of some common types of helical gears:
- Parallel Helical Gears: Parallel helical gears are the most commonly used type of helical gears. In this configuration, two helical gears with parallel axes are meshed together. They transmit power and motion between parallel shafts. Parallel helical gears provide smooth operation, high load-carrying capacity, and efficient power transmission.
- Double Helical Gears (Herringbone Gears): Double helical gears, also known as herringbone gears, have two sets of helical teeth that are placed in a V-shaped configuration. The V-shaped teeth face each other, with a groove or gap in the middle. This design cancels out the axial thrust that is generated by the helical gear’s inclined teeth. Double helical gears are often used in applications that require high torque transmission and axial load balancing, such as heavy machinery and marine propulsion systems.
- Crossed Helical Gears (Screw Gears): Crossed helical gears, also referred to as screw gears, involve the meshing of two helical gears with non-parallel and non-intersecting axes. The gears are oriented at an angle to each other, typically 90 degrees. Crossed helical gears are used in applications where shafts intersect or when a compact and non-parallel gear arrangement is required. They are commonly found in hand drills, speedometers, and some mechanical watches.
- Skew Gears: Skew gears are a type of helical gear in which the gear teeth are cut at an angle to the gear axis. The angle of the teeth can vary, allowing for different degrees of skew. Skew gears are used in applications where the axes of the mating gears are neither parallel nor intersecting. They can transmit power between non-parallel and non-intersecting shafts while accommodating misalignments.
- Helical Rack and Pinion: A helical rack and pinion system consists of a helical gear (pinion) that meshes with a linear gear (rack). The pinion is a cylindrical gear with helical teeth, while the rack is a straight bar with teeth that mesh with the pinion. This configuration is commonly used in applications that require linear motion, such as CNC machines, robotics, and rack and pinion steering systems in automobiles.
- Variable Helix Gears: Variable helix gears have a unique tooth profile where the helix angle varies along the face width of the gear. The varying helix angle helps to reduce noise, vibration, and backlash while maintaining smooth operation and load distribution. These gears are often used in high-performance applications where noise reduction and precise motion control are critical.
The specific type of helical gear used depends on factors such as the application requirements, load conditions, space limitations, and desired performance characteristics. Manufacturers often provide various options and customizations to meet specific needs.
It’s important to note that the design and manufacturing of helical gears require careful consideration of factors such as tooth profile, helix angle, lead angle, module or pitch, pressure angle, and material selection. These factors ensure proper gear meshing, load distribution, and efficient power transmission.
In summary, different types of helical gears, including parallel helical gears, double helical gears (herringbone gears), crossed helical gears (screw gears), skew gears, helical rack and pinion systems, and variable helix gears, are available to cater to a wide range of applications. Each type has its unique characteristics and advantages, allowing for optimized performance and reliable power transmission in various industries and machinery.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09